Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, and the skeleton
- PMID: 18436706
- PMCID: PMC2726838
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2007-0036
Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, and the skeleton
Abstract
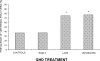
GH and IGF-I are important regulators of bone homeostasis and are central to the achievement of normal longitudinal bone growth and bone mass. Although GH may act directly on skeletal cells, most of its effects are mediated by IGF-I, which is present in the systemic circulation and is synthesized by peripheral tissues. The availability of IGF-I is regulated by IGF binding proteins. IGF-I enhances the differentiated function of the osteoblast and bone formation. Adult GH deficiency causes low bone turnover osteoporosis with high risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures, and the low bone mass can be partially reversed by GH replacement. Acromegaly is characterized by high bone turnover, which can lead to bone loss and vertebral fractures, particularly in patients with coexistent hypogonadism. GH and IGF-I secretion are decreased in aging individuals, and abnormalities in the GH/IGF-I axis play a role in the pathogenesis of the osteoporosis of anorexia nervosa and after glucocorticoid exposure.
Figures


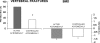
References
-
- Ohlsson C, Bengtsson BA, Isaksson OG, Andreassen TT, Slootweg MC 1998 Growth hormone and bone. Endocr Rev 19:55–79 - PubMed
-
- Baroncelli GI, Bertelloni S, Sodini F, Saggese G 2003 Acquisition of bone mass in normal individuals and in patients with growth hormone deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 16(Suppl 2):327–335 - PubMed
-
- Monson JP, Drake WM, Carroll PV, Weaver JU, Rodriguez-Arnao J, Savage MO 2002 Influence of growth hormone on accretion of bone mass. Horm Res 58(Suppl 1):52–56 - PubMed
-
- Nilsson O, Marino R, De Luca F, Phillip M, Baron J 2005 Endocrine regulation of the growth plate. Horm Res 64:157–165 - PubMed
-
- Woods KA, Camacho-Hubner C, Savage MO, Clark AJ 1996 Intrauterine growth retardation and postnatal growth failure associated with deletion of the insulin-like growth factor I gene. N Engl J Med 335:1363–1367 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

