Discovering sequence motifs with arbitrary insertions and deletions
- PMID: 18437229
- PMCID: PMC2323616
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000071
Discovering sequence motifs with arbitrary insertions and deletions
Abstract
BIOLOGY IS ENCODED IN MOLECULAR SEQUENCES: deciphering this encoding remains a grand scientific challenge. Functional regions of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences often exhibit characteristic but subtle motifs; thus, computational discovery of motifs in sequences is a fundamental and much-studied problem. However, most current algorithms do not allow for insertions or deletions (indels) within motifs, and the few that do have other limitations. We present a method, GLAM2 (Gapped Local Alignment of Motifs), for discovering motifs allowing indels in a fully general manner, and a companion method GLAM2SCAN for searching sequence databases using such motifs. glam2 is a generalization of the gapless Gibbs sampling algorithm. It re-discovers variable-width protein motifs from the PROSITE database significantly more accurately than the alternative methods PRATT and SAM-T2K. Furthermore, it usefully refines protein motifs from the ELM database: in some cases, the refined motifs make orders of magnitude fewer overpredictions than the original ELM regular expressions. GLAM2 performs respectably on the BAliBASE multiple alignment benchmark, and may be superior to leading multiple alignment methods for "motif-like" alignments with N- and C-terminal extensions. Finally, we demonstrate the use of GLAM2 to discover protein kinase substrate motifs and a gapped DNA motif for the LIM-only transcriptional regulatory complex: using GLAM2SCAN, we identify promising targets for the latter. GLAM2 is especially promising for short protein motifs, and it should improve our ability to identify the protein cleavage sites, interaction sites, post-translational modification attachment sites, etc., that underlie much of biology. It may be equally useful for arbitrarily gapped motifs in DNA and RNA, although fewer examples of such motifs are known at present. GLAM2 is public domain software, available for download at http://bioinformatics.org.au/glam2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

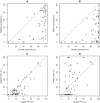

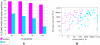

References
-
- Kim NK, Tharakaraman K, Spouge JL. Adding sequence context to a Markov background model improves the identification of regulatory elements. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2870–2875. - PubMed
-
- Roth FP, Hughes JD, Estep PW, Church GM. Finding DNA regulatory motifs within unaligned noncoding sequences clustered by whole-genome mRNA quantitation. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16:939–945. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Brutlag DL, Liu JS. BioProspector: discovering conserved DNA motifs in upstream regulatory regions of co-expressed genes. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2001:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Liu XS, Brutlag DL, Liu JS. An algorithm for finding protein-DNA binding sites with applications to chromatin-immunoprecipitation microarray experiments. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:835–839. - PubMed
-
- van Helden J, André B, Collado-Vides J. Extracting regulatory sites from the upstream region of yeast genes by computational analysis of oligonucleotide frequencies. J Mol Biol. 1998;281:827–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

