Know your place: neural processing of social hierarchy in humans
- PMID: 18439411
- PMCID: PMC2430590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.01.025
Know your place: neural processing of social hierarchy in humans
Abstract
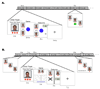
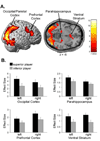
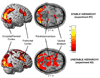
Social hierarchies guide behavior in many species, including humans, where status also has an enormous impact on motivation and health. However, little is known about the underlying neural representation of social hierarchies in humans. In the present study, we identify dissociable neural responses to perceived social rank using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in an interactive, simulated social context. In both stable and unstable social hierarchies, viewing a superior individual differentially engaged perceptual-attentional, saliency, and cognitive systems, notably dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. In the unstable hierarchy setting, additional regions related to emotional processing (amygdala), social cognition (medial prefrontal cortex), and behavioral readiness were recruited. Furthermore, social hierarchical consequences of performance were neurally dissociable and of comparable salience to monetary reward, providing a neural basis for the high motivational value of status. Our results identify neural mechanisms that may mediate the enormous influence of social status on human behavior and health.
Figures


Comment in
-
For love or money: a common neural currency for social and monetary reward.Neuron. 2008 Apr 24;58(2):164-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.005. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18439400
References
-
- Abler B, Walter H, Erk S. Neural correlates of frustration. Neuroreport. 2005;16:669–672. - PubMed
-
- Adolphs R. Is the human amygdala specialized for processing social information? Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2003;985:326–340. - PubMed
-
- Aminoff E, Gronau N, Bar M. The parahippocampal cortex mediates spatial and nonspatial associations. Cereb. Cortex. 2007;17:1493–1503. - PubMed
-
- Amodio DM, Frith CD. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006;7:268–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

