Chlorhexidine release and water sorption characteristics of chlorhexidine-incorporated hydrophobic/hydrophilic resins
- PMID: 18439668
- PMCID: PMC3886642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dental.2008.03.011
Chlorhexidine release and water sorption characteristics of chlorhexidine-incorporated hydrophobic/hydrophilic resins
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to evaluate chlorhexidine release from unfilled non-solvated methacrylate-based resins of increasing hydrophilicity and to examine relationships among Hoy's solubility parameters, water sorption, solubility and the rate of chlorhexidine release.
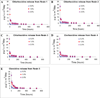
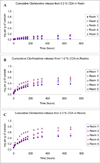
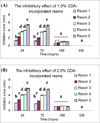
Methods: Resin discs were prepared from light-cured, experimental resin blends (R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5) containing 0.0, 0.2, 1.0 and 2.0 wt.% chlorhexidine diacetate (CDA). Discs were immersed in distilled water at 37 degrees C, and mass changes were recorded at different periods. Spectral measurements were made to follow change in optical densities of storage solution to examine chlorhexidine release kinetics. After a 28-day period, water sorption, solubility, and the cumulative chlorhexidine release were obtained. Additionally, antibacterial study was performed by observing the presence of inhibition zone against Streptococcus mutans.
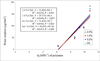
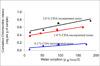
Results: The most hydrophilic resin (R5) exhibited the highest chlorhexidine release rate. The most hydrophobic resin (R1) exhibited the lowest rate. However, no inhibition zone was produced by any specimens stored in water for 2 weeks. The addition of CDA increased solubility significantly but had no effect on water sorption. Significant positive correlations were seen between water sorption and the cumulative chlorhexidine release.
Significance: Chlorhexidine release from resins may be related to water-induced swelling, which in turn is enhanced by the hydrophilicity of cured polymer matrix.
Figures


References
-
- Tay FR, Pashley DH. Dental adhesives of the future. J Adhes Dent. 2002;4:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Van Meerbeek B, De Munck J, Yoshida Y. Buonocore memorial lecture. Adhesion to enamel and dentin: current status and future challenges. Oper Dent. 2003;28:215–235. - PubMed
-
- Pashley DH. Dentin: a dynamic substrate--a review. Scanning Microsc. 1989;3:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Kidd EAM. Microleakage: a review. J Dent. 1976;4:199–205. - PubMed
-
- Imazato S, Kinomoto Y, Tarumi H, Torii M, Russell RRB, McCabe JF. Incorporation of antibacterial monomer MDPB in dentin primer. J Dent Res. 1994;73:1437–1444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

