AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint
- PMID: 18439900
- PMCID: PMC2674027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.03.003
AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint
Abstract
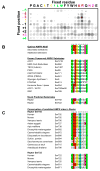
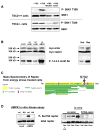
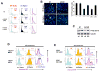
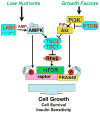
AMPK is a highly conserved sensor of cellular energy status that is activated under conditions of low intracellular ATP. AMPK responds to energy stress by suppressing cell growth and biosynthetic processes, in part through its inhibition of the rapamycin-sensitive mTOR (mTORC1) pathway. AMPK phosphorylation of the TSC2 tumor suppressor contributes to suppression of mTORC1; however, TSC2-deficient cells remain responsive to energy stress. Using a proteomic and bioinformatics approach, we sought to identify additional substrates of AMPK that mediate its effects on growth control. We report here that AMPK directly phosphorylates the mTOR binding partner raptor on two well-conserved serine residues, and this phosphorylation induces 14-3-3 binding to raptor. The phosphorylation of raptor by AMPK is required for the inhibition of mTORC1 and cell-cycle arrest induced by energy stress. These findings uncover a conserved effector of AMPK that mediates its role as a metabolic checkpoint coordinating cell growth with energy status.
Figures



Comment in
-
AMPK and Raptor: matching cell growth to energy supply.Mol Cell. 2008 May 9;30(3):263-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.04.012. Mol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18471972
References
-
- Baena-Gonzalez E, Rolland F, Thevelein JM, Sheen J. A central integrator of transcription networks in plant stress and energy signalling. Nature. 2007;448:938–942. - PubMed
-
- Baugh LR, Sternberg PW. DAF-16/FOXO regulates transcription of cki-1/Cip/Kip and repression of lin-4 during C. elegans L1 arrest. Curr Biol. 2006;16:780–785. - PubMed
-
- Bridges D, Moorhead GB. 14-3-3 proteins: a number of functions for a numbered protein. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:re10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

