NF-kappaB and cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms
- PMID: 18440219
- PMCID: PMC2587362
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2008.01.020
NF-kappaB and cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms
Abstract
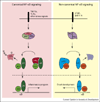
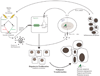
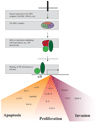
A connection between inflammation and carcinogenesis has long been known, but the precise mechanisms are just beginning to be understood. NF-kappaB proteins, transcription factors which integrate stress signals and orchestrate immune responses, have also recently been linked to carcinogenesis. Hallmarks of cancer development include self-sufficiency in growth signals, insensitivity to growth-inhibitors, evasion of apoptosis, limitless replicative potential, tissue invasion and metastasis, and sustained angiogenesis. NF-kappaB signaling has been implicated in each of these hallmarks, and recent experimental studies have illuminated the mechanistic pathways by which NF-kappaB signaling contributes to these aspects of carcinogenesis. This review will focus on recent experimental data supporting the hypothesis that inflammation promotes carcinogenesis, and that NF-kappaB signaling is at the heart of such inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NF-kappaB in solid tumors.Biochem Pharmacol. 2006 Oct 30;72(9):1142-52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.032. Epub 2006 Sep 7. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16956585 Review.
-
Ion channels and the hallmarks of cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2010 Mar;16(3):107-21. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.01.005. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Trends Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20167536 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of curcumins suppressing effects on tumorigenesis, angiogenesis and metastasis, focusing on NF-κB pathway.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Apr;28:21-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2015.12.004. Epub 2016 Jan 2. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 26774676 Review.
-
NF-kappaB and IKK as therapeutic targets in cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2006 May;13(5):738-47. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4401877. Cell Death Differ. 2006. PMID: 16485028 Review.
-
Cryptopleurine targets NF-κB pathway, leading to inhibition of gene products associated with cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e40355. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040355. Epub 2012 Jun 29. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22768286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Modulates Oxidative Stress, Fibrosis, and Apoptosis in Drug-Resistant Cancer Cell Lines.Life (Basel). 2022 Sep 13;12(9):1427. doi: 10.3390/life12091427. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36143462 Free PMC article.
-
Misregulation of PPAR Functioning and Its Pathogenic Consequences Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Human Obesity.PPAR Res. 2012;2012:107434. doi: 10.1155/2012/107434. Epub 2012 Dec 9. PPAR Res. 2012. PMID: 23304111 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of intestinal epithelial cell STAT3 promotes T-lymphocyte STAT3 activation and chronic colitis following acute dextran sodium sulfate injury in mice.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 Mar;19(3):512-25. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e31828028ad. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013. PMID: 23429443 Free PMC article.
-
PPAR Ligands Function as Suppressors That Target Biological Actions of HMGB1.PPAR Res. 2016;2016:2612743. doi: 10.1155/2016/2612743. Epub 2016 Aug 2. PPAR Res. 2016. PMID: 27563308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-130b, an onco-miRNA in bladder cancer, is directly regulated by NF-κB and sustains NF-κB activation by decreasing Cylindromatosis expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):48547-48561. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10423. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27391066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karin M, Lawrence T, Nizet V. Innate immunity gone awry: linking microbial infections to chronic inflammation and cancer. Cell. 2006;124(4):823–835. - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW. NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(4):301–310. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357(9255):539–545. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. International Journal of Cancer. 2001;94(2):153–156. - PubMed
-
- Kuper H, Adami HO, Trichopoulos D. Infections as a major preventable cause of human cancer. J Intern Med. 2000;248(3):171–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources