Dystrophin-deficient cardiomyopathy in mouse: expression of Nox4 and Lox are associated with fibrosis and altered functional parameters in the heart
- PMID: 18440230
- PMCID: PMC2430663
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2008.03.008
Dystrophin-deficient cardiomyopathy in mouse: expression of Nox4 and Lox are associated with fibrosis and altered functional parameters in the heart
Abstract
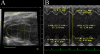
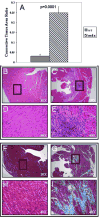
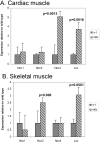
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD; dystrophin-deficiency) causes dilated cardiomyopathy in the second decade of life in affected males. We studied the dystrophin-deficient mouse heart (mdx) using high-frequency echocardiography, histomorphometry, and gene expression profiling. Heart dysfunction was prominent at 9-10months of age and showed significantly increased LV internal diameter (end systole) and decreased posterior wall thickness. This cardiomyopathy was associated with a 30% decrease in shortening fraction. Histologically, there was a 10-fold increase in connective tissue volume (fibrosis). mRNA profiling with RT-PCR validation showed activation of key pro-fibrotic genes, including Nox4 and Lox. The Nox gene family expression differed in mdx heart and skeletal muscle, where Nox2 was specifically induced in skeletal muscle while Nox4 was specifically induced in heart. This is the first report of an altered profibrotic gene expression profile in cardiac tissue of dystrophic mice showing echocardiographic evidence of cardiomyopathy.
Figures
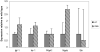
References
-
- Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM. Dystrophin, the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987;51:919–928. - PubMed
-
- Gilroy J, Cahalan JL, Berman R, Newman M. Cardiac and pulmonary complications in Duchenne’s progressive muscular dystrophy. Circulation. 1963;27:484–493. - PubMed
-
- De Kermadec JM, Becane HM, Chenard A, Tertrain F, Weiss Y. Prevalence of left ventricular systolic dysfunction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy: an echocardiographic study. Am Heart J. 1994;127:618–23. - PubMed
-
- Kirchmann C, Kececioglu D, Korinthenberg R, Dittrich S. Echocardiographic and electrocardiographic findings of cardiomyopathy in Duchenne and Becker-Kiener muscular dystrophies. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005;26:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Gulati S, Saxena A, Kumar V, Kalra V. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Prevalence and Patterns of Cardiac Involvement. Indian J Pediatr. 2005;72:389–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

