3D visualization software to analyze topological outcomes of topoisomerase reactions
- PMID: 18440983
- PMCID: PMC2441796
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkn192
3D visualization software to analyze topological outcomes of topoisomerase reactions
Abstract
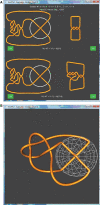
The action of various DNA topoisomerases frequently results in characteristic changes in DNA topology. Important information for understanding mechanistic details of action of these topoisomerases can be provided by investigating the knot types resulting from topoisomerase action on circular DNA forming a particular knot type. Depending on the topological bias of a given topoisomerase reaction, one observes different subsets of knotted products. To establish the character of topological bias, one needs to be aware of all possible topological outcomes of intersegmental passages occurring within a given knot type. However, it is not trivial to systematically enumerate topological outcomes of strand passage from a given knot type. We present here a 3D visualization software (TopoICE-X in KnotPlot) that incorporates topological analysis methods in order to visualize, for example, knots that can be obtained from a given knot by one intersegmental passage. The software has several other options for the topological analysis of mechanisms of action of various topoisomerases.
Figures
References
-
- Sogo JM, Stasiak A, Martinez-Robles ML, Krimer DB, Hernandez P, Schvartzman JB. Formation of knots in partially replicated DNA molecules. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;286:637–643. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. Moving one DNA double helix through another by a type II DNA topoisomerase: the story of a simple molecular machine. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1998;31:107–144. - PubMed
-
- Corbett KD, Berger JM. Structure, molecular mechanisms, and evolutionary relationships in DNA topoisomerases. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 2004;33:95–118. - PubMed

