Visualization of polarized membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase activity in live cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer imaging
- PMID: 18441011
- PMCID: PMC2427332
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M709872200
Visualization of polarized membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase activity in live cells by fluorescence resonance energy transfer imaging
Abstract
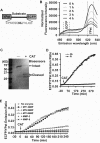
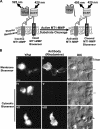
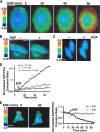
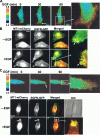
Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) plays a critical role in cancer cell biology by proteolytically remodeling the extracellular matrix. Utilizing fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) imaging, we have developed a novel biosensor, with its sensing element anchoring at the extracellular surface of cell membrane, to visualize MT1-MMP activity dynamically in live cells with subcellular resolution. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induced significant FRET changes in cancer cells expressing MT1-MMP, but not in MT1-MMP-deficient cells. EGF-induced FRET changes in MT1-MMP-deficient cells could be restored after reconstituting with wild-type MT1-MMP, but not MMP-2, MMP-9, or inactive MT1-MMP mutants. Deletion of the transmembrane domain in the biosensor or treatment with tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2, a cell-impermeable MT1-MMP inhibitor, abolished the EGF-induced FRET response, indicating that MT1-MMP acts at the cell surface to generate FRET changes. In response to EGF, active MT1-MMP was directed to the leading edge of migrating cells along micropatterned fibronectin stripes, in tandem with the local accumulation of the EGF receptor, via a process dependent upon an intact cytoskeletal network. Hence, the MT1-MMP biosensor provides a powerful tool for characterizing the molecular processes underlying the spatiotemporal regulation of this critical class of enzymes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetically encoded fluorescent biosensors for live-cell imaging of MT1-MMP protease activity.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1071:163-74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-622-1_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24052388 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous visualization of protumorigenic Src and MT1-MMP activities with fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 15;70(6):2204-12. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3698. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20197470 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative FRET imaging to visualize the invasiveness of live breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058569. Epub 2013 Mar 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23516511 Free PMC article.
-
The Diverse Pathways for Cell Surface MT1-MMP Localization in Migratory Cells.Cells. 2025 Jan 31;14(3):209. doi: 10.3390/cells14030209. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane-type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), lipid metabolism, and therapeutic implications.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Oct 21;13(7):513-526. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab048. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34297054 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monitoring and Inhibiting MT1-MMP during Cancer Initiation and Progression.Cancers (Basel). 2014 Feb 17;6(1):416-35. doi: 10.3390/cancers6010416. Cancers (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24549119 Free PMC article.
-
Directed Evolution to Engineer Monobody for FRET Biosensor Assembly and Imaging at Live-Cell Surface.Cell Chem Biol. 2018 Apr 19;25(4):370-379.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 27. Cell Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29396288 Free PMC article.
-
Decipher the dynamic coordination between enzymatic activity and structural modulation at focal adhesions in living cells.Sci Rep. 2014 Jul 24;4:5756. doi: 10.1038/srep05756. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25056908 Free PMC article.
-
Phase differential enhancement of FLIM to distinguish FRET components of a biosensor for monitoring molecular activity of Membrane Type 1 Matrix Metalloproteinase in live cells.J Fluoresc. 2011 Jul;21(4):1763-77. doi: 10.1007/s10895-011-0871-x. Epub 2011 Apr 26. J Fluoresc. 2011. PMID: 21519891 Free PMC article.
-
Red-shifted fluorescent proteins monitor enzymatic activity in live HT-1080 cells with fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM).J Microsc. 2012 Oct;248(1):77-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.2012.03652.x. J Microsc. 2012. PMID: 22971220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seiki, M. (2003) Cancer Lett. 194 1-11 - PubMed
-
- Visse, R., and Nagase, H. (2003) Circ. Res. 92 827-839 - PubMed
-
- Deryugina, E. I., and Quigley, J. P. (2006) Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25 9-34 - PubMed
-
- Deryugina, E. I., Ratnikov, B., Monosov, E., Postnova, T. I., DiScipio, R., Smith, J. W., and Strongin, A. Y. (2001) Exp. Cell Res. 263 209-223 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

