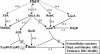
Regulatory network controlling extracellular proteins in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: FlhDC, the master regulator of flagellar genes, activates rsmB regulatory RNA production by affecting gacA and hexA (lrhA) expression
- PMID: 18441056
- PMCID: PMC2446818
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01828-07
Regulatory network controlling extracellular proteins in Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora: FlhDC, the master regulator of flagellar genes, activates rsmB regulatory RNA production by affecting gacA and hexA (lrhA) expression
Abstract
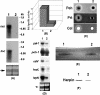
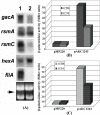
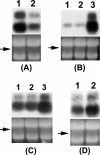
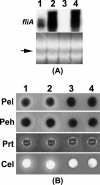
Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora produces an array of extracellular proteins (i.e., exoproteins), including plant cell wall-degrading enzymes and Harpin, an effector responsible for eliciting hypersensitive reaction. Exoprotein genes are coregulated by the quorum-sensing signal, N-acyl homoserine lactone, plant signals, an assortment of transcriptional factors/regulators (GacS/A, ExpR1, ExpR2, KdgR, RpoS, HexA, and RsmC) and posttranscriptional regulators (RsmA, rsmB RNA). rsmB RNA production is positively regulated by GacS/A, a two-component system, and negatively regulated by HexA (PecT in Erwinia chrysanthemi; LrhA [LysR homolog A] in Escherichia coli) and RsmC, a putative transcriptional adaptor. While free RsmA, an RNA-binding protein, promotes decay of mRNAs of exoprotein genes, binding of RsmA with rsmB RNA neutralizes the RsmA effect. In the course of studies of GacA regulation, we discovered that a locus bearing strong homology to the flhDC operon of E. coli also controls extracellular enzyme production. A transposon insertion FlhDC(-) mutant produces very low levels of pectate lyase, polygalacturonase, cellulase, protease, and E. carotovora subsp. carotovora Harpin (Harpin(Ecc)) and is severely attenuated in its plant virulence. The production of these exoproteins is restored in the mutant carrying an FlhDC(+) plasmid. Sequence analysis and transcript assays disclosed that the flhD operon of E. carotovora subsp. carotovora, like those of other enterobacteria, consists of flhD and flhC. Complementation analysis revealed that the regulatory effect requires functions of both flhD and flhC products. The data presented here show that FlhDC positively regulates gacA, rsmC, and fliA and negatively regulates hexA (lrhA). Evidence shows that FlhDC controls extracellular protein production through cumulative effects on hexA and gacA. Reduced levels of GacA and elevated levels of HexA in the FlhDC(-) mutant are responsible for the inhibition of rsmB RNA production, a condition conducive to the accumulation of free RsmA. Indeed, studies with an RsmA(-) FlhDC(-) double mutant and multiple copies of rsmB(+) DNA establish that the negative effect of FlhDC deficiency is exerted via RsmA. The FlhDC-mediated regulation of fliA has no bearing on exoprotein production in E. carotovora subsp. carotovora. Our observations for the first time establish a regulatory connection between FlhDC, HexA, GacA, and rsmB RNA in the context of the exoprotein production and virulence of E. carotovora subsp. carotovora.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Effects of the two-component system comprising GacA and GacS of Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora on the production of global regulatory rsmB RNA, extracellular enzymes, and harpinEcc.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2001 Apr;14(4):516-26. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.4.516. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2001. PMID: 11310739
-
rsmC of the soft-rotting bacterium Erwinia carotovora subsp. carotovora negatively controls extracellular enzyme and harpin(Ecc) production and virulence by modulating levels of regulatory RNA (rsmB) and RNA-binding protein (RsmA).J Bacteriol. 1999 Oct;181(19):6042-52. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.19.6042-6052.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10498717 Free PMC article.
-
hexA of Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora strain Ecc71 negatively regulates production of RpoS and rsmB RNA, a global regulator of extracellular proteins, plant virulence and the quorum-sensing signal, N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone.Environ Microbiol. 2000 Apr;2(2):203-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2000.00093.x. Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11220306
-
Global regulation by the small RNA-binding protein CsrA and the non-coding RNA molecule CsrB.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Sep;29(6):1321-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.01021.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9781871 Review.
-
Two-component system GacS/GacA, a global response regulator of bacterial physiological behaviors.Eng Microbiol. 2022 Oct 5;3(1):100051. doi: 10.1016/j.engmic.2022.100051. eCollection 2023 Mar. Eng Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 39628522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of the plant pathogen Xanthomonas identifies sRNAs with putative virulence functions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(5):2020-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr904. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22080557 Free PMC article.
-
Innovation and Application of the Type III Secretion System Inhibitors in Plant Pathogenic Bacteria.Microorganisms. 2020 Dec 9;8(12):1956. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8121956. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 33317075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of plant phenolic compounds that act as type III secretion system inhibitors or inducers of the fire blight pathogen, Erwinia amylovora.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Sep;79(18):5424-36. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00845-13. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23770912 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the flhD gene of Escherichia coli K-12 do not cause the reported effect on cell division.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010 Aug 1;309(1):94-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02021.x. Epub 2010 May 20. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20546312 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Inhibition of Pectobacterium brasiliense Virulence by the Citrus Flavanone Naringenin.J Agric Food Chem. 2025 Aug 20;73(33):20792-20809. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5c04312. Epub 2025 Aug 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40767039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldridge, P., and K. T. Hughes. 2002. Regulation of flagellar assembly. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 5160-165. - PubMed
-
- Barembruch, C., and R. Hengge. 2007. Cellular levels and activity of the flagellar sigma factor FliA of Escherichia coli are controlled by FlgM-modulated proteolysis. Mol. Microbiol. 6576-89. - PubMed
-
- Barras, F., F. Van Gijsegem, and A. K. Chatterjee. 1994. Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 32201-234.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

