Metalloelastase in lungs and alveolar macrophages is modulated by extracellular substance P in mice
- PMID: 18441096
- PMCID: PMC2494786
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00282.2007
Metalloelastase in lungs and alveolar macrophages is modulated by extracellular substance P in mice
Abstract
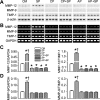
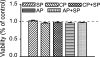
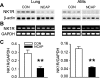
Metalloelastase (MMP-12), mainly produced by macrophages, has been shown to play a key role in the pathogenesis of emphysema in animal models. Chronic cigarette smoke increases pulmonary MMP-12, which is closely correlated with an elevation of pulmonary substance P (SP). Because alveolar macrophages (AMs) contain the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R), we tested whether SP was able to trigger the upregulation of MMP-12 synthesis in AMs by acting on the NK1R. AMs isolated from bronchoalveolar lavage cells in C3H/HeN mice were cultured with control medium or SP that was coupled without or with NK1R antagonists (CP-99,994 or aprepitant) for 24 h. We found that SP significantly increased the mRNA of MMP-12 and NK1R by 11-fold and 82%, respectively, in AMs (P<0.05), and these responses were abolished by NK1R antagonists with little change in the cells' viability. Because pulmonary SP is primarily released by bronchopulmonary C-fibers (PCFs), we further asked whether destruction of PCFs would reduce SP and MMP-12. Two groups of mice were pretreated with vehicle and neonatal capsaicin (NCAP) to degenerate PCFs, respectively. Our results show that NCAP treatment significantly decreased mRNA and protein levels of SP associated with a reduction NK1R and MMP-12 in the lungs and AMs. These findings suggest that SP has a modulatory effect on pulmonary MMP-12 by acting on NK1R to trigger MMP-12 syntheses in the AMs.
Figures
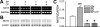
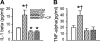
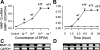


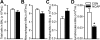
Similar articles
-
Prenatal nicotinic exposure upregulates pulmonary C-fiber NK1R expression to prolong pulmonary C-fiber-mediated apneic response.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 1;290:107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26524655 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neurogenic substance P in overexpression of alveolar macrophages' neurokinin 1 receptor in mice exposed to cigarette smoke.Exp Lung Res. 2010 May;36(4):243-54. doi: 10.3109/01902140903398275. Exp Lung Res. 2010. PMID: 20426532
-
Cigarette smoke-induced hypercapnic emphysema in C3H mice is associated with increases of macrophage metalloelastase and substance P in the lungs.Exp Lung Res. 2007 Jun-Jul;33(5):197-215. doi: 10.1080/01902140701459514. Exp Lung Res. 2007. PMID: 17620183
-
Increased surfactant protein-D and foamy macrophages in smoking-induced mouse emphysema.Respirology. 2007 Mar;12(2):191-201. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.01009.x. Respirology. 2007. PMID: 17298450 Review.
-
Substance P and the Neurokinin-1 Receptor: The New CRF.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;136:151-175. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 29056150 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal nicotinic exposure upregulates pulmonary C-fiber NK1R expression to prolong pulmonary C-fiber-mediated apneic response.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016 Jan 1;290:107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26524655 Free PMC article.
-
Early matrix metalloproteinase-12 inhibition worsens post-myocardial infarction cardiac dysfunction by delaying inflammation resolution.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Apr 15;185:198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.054. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25797678 Free PMC article.
-
Neural control of airway inflammation.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009 Nov;9(6):484-90. doi: 10.1007/s11882-009-0071-9. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2009. PMID: 19814922 Review.
-
The in vivo efficacy and side effect pharmacology of GS-5759, a novel bifunctional phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor and long-acting β 2-adrenoceptor agonist in preclinical animal species.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014 Aug;2(4):e00046. doi: 10.1002/prp2.46. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2014. PMID: 25505595 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases contribute to the regulation of chemokine expression and pulmonary inflammation in Cryptococcus infection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Mar;183(3):431-40. doi: 10.1111/cei.12725. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26445891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardelli C, Gunella G, Varsaldi F, Balbo P, Del Boca E, Bernardone IS, Amoruso A, Brunelleschi S. Expression of functional NK1 receptors in human alveolar macrophages: superoxide anion production, cytokine release and involvement of NF-kappaB pathway. Br J Pharmacol 145: 385–396, 2005. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brylla E, Aust G, Geyer M, Uckermann O, Loffler S, Spanel-Borowski K. Coexpression of preprotachykinin A and B transcripts in the bovine corpus luteum and evidence for functional neurokinin receptor activity in luteal endothelial cells and ovarian macrophages. Regul Pept 125: 125–133, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Chu L, Peng JW, Jiang HY, Zeng QF. Expression of early growth response gene-1 in macrophages stimulated by silicon dioxide [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 32: 558–562, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Churg A, Wang RD, Tai H, Wang X, Xie C, Wright JL. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha drives 70% of cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in the mouse. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 170: 492–498, 2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

