Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates sympathetic responses to muscle stretch in humans
- PMID: 18441194
- PMCID: PMC3531047
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.91505.2007
Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates sympathetic responses to muscle stretch in humans
Abstract
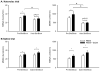
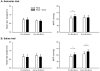
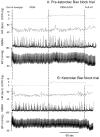
Passive muscle stretch performed during a period of post-exercise muscle ischemia (PEMI) increases muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA), and this suggests that the muscle metabolites may sensitize mechanoreceptors in healthy humans. However, the responsible substance(s) has not been studied thoroughly in humans. Human and animal studies suggest that cyclooxygenase products sensitize muscle mechanoreceptors. Thus we hypothesized that local cyclooxygenase inhibition in exercising muscles could attenuate MSNA responses to passive muscle stretch during PEMI. Blood pressure (Finapres), heart rate, and MSNA (microneurography) responses to passive muscle stretch were assessed in 13 young healthy subjects during PEMI before and after cyclooxygenase inhibition, which was accomplished by a local infusion of 6 mg ketorolac tromethamine in saline via Bier block. In the second experiment, the same amount of saline was infused via the Bier block. Ketorolac Bier block decreased prostaglandin synthesis to approximately 34% of the baseline. Before ketorolac Bier block, passive muscle stretch evoked significant increases in MSNA (P < 0.005) and mean arterial blood pressure (P < 0.02). After ketorolac Bier block, passive muscle stretch did not evoke significant responses in MSNA (P = 0.11) or mean arterial blood pressure (P = 0.83). Saline Bier block had no effect on the MSNA or blood pressure response to ischemic stretch. These observations indicate that cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates MSNA responses seen during PEMI and suggest that cyclooxygenase products sensitize the muscle mechanoreceptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Local prostaglandin blockade attenuates muscle mechanoreflex-mediated renal vasoconstriction during muscle stretch in humans.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 May;294(5):H2184-90. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00948.2007. Epub 2008 Mar 7. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18326807 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of the cyclooxygenase products in evoking sympathetic activation in exercise.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):H1861-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00258.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17604332 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cyclooxygenase products sensitize muscle mechanoreceptors in humans with heart failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Apr;294(4):H1956-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01304.2007. Epub 2008 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18296564 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of muscle metabolites on responses of muscle sympathetic nerve activity to mechanoreceptor(s) stimulation in healthy humans.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):R458-66. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00475.2007. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18003788
-
[Application of microneurography to circulatory disorders].Brain Nerve. 2009 Mar;61(3):270-6. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19301597 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of cyclooxygenase attenuates the blood pressure response to plantar flexion exercise in peripheral arterial disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 Aug 1;309(3):H523-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00267.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26055794 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Cyclooxygenase Inhibition on Peripheral Venous Distension Reflex in Healthy Humans.Hypertension. 2023 May;80(5):1102-1109. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.20506. Epub 2023 Mar 21. Hypertension. 2023. PMID: 36942572 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic acidosis augments exercise pressor responses in chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):R312-R318. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00076.2019. Epub 2019 May 29. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31141417 Free PMC article.
-
A role for nitric oxide within the nucleus tractus solitarii in the development of muscle mechanoreflex dysfunction in hypertension.Exp Physiol. 2012 Dec;97(12):1292-304. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.065433. Epub 2012 May 11. Exp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22581746 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the mechanisms of cyclooxygenase-mediated mechanoreflex sensitization in a rat model of simulated peripheral artery disease.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Nov 1;317(5):H1050-H1061. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00399.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31469294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adreani CM, Hill JM, Kaufman MP. Responses of group III and IV muscle afferents to dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1997;82:1811–1817. - PubMed
-
- Adreani CM, Kaufman MP. Effect of arterial occlusion on responses of group III and IV afferents to dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1998;84:1827–1833. - PubMed
-
- Batman BA, Hardy JC, Leuenberger UA, Smith MB, Yang QX, Sinoway LI. Sympathetic nerve activity during prolonged rhythmic forearm exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1994;76:1077–1081. - PubMed
-
- Baum K, Selle K, Leyk D, Essfeld D. Comparison of blood pressure and heart rate responses to isometric exercise and passive muscle stretch in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1995;70:240–245. - PubMed
-
- Bell MP, White MJ. Cardiovascular responses to external compression of human calf muscle vary during graded metaboreflex stimulation. Exp Physiol. 2005;90:383–391. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

