Inhibitory effect of D1-like and D3 dopamine receptors on norepinephrine-induced proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 18441198
- PMCID: PMC2772091
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.01344.2007
Inhibitory effect of D1-like and D3 dopamine receptors on norepinephrine-induced proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
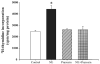
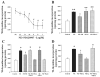
The sympathetic nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of blood pressure. There is increasing evidence for positive and negative interactions between dopamine and adrenergic receptors; the activation of the alpha-adrenergic receptor induces vasoconstriction, whereas the activation of dopamine receptor induces vasorelaxation. We hypothesize that the D1-like receptor and/or D3 receptor also inhibit alpha1-adrenergic receptor-mediated proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). In this study, VSMC proliferation was determined by measuring [3H]thymidine incorporation, cell number, and uptake of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT). Norepinephrine increased VSMC number and MTT uptake, as well as [3H]thymidine incorporation via the alpha1-adrenergic receptor in aortic VSMCs from Sprague-Dawley rats. The proliferative effects of norepinephrine were attenuated by the activation of D1-like receptors or D3 receptors, although a D1-like receptor agonist, fenoldopam, and a D3 receptor agonist, PD-128907, by themselves, at low concentrations, had no effect on VSMC proliferation. Simultaneous stimulation of both D1-like and D3 receptors had an additive inhibitory effect. The inhibitory effect of D3 receptor was via protein kinase A, whereas the D1-like receptor effect was via protein kinase C-zeta. The interaction between alpha1-adrenergic and dopamine receptors, especially D1-like and D3 receptors in VSMCs, could be involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of D1-like dopamine receptors on neuropeptide Y-induced proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Hypertens Res. 2015 Dec;38(12):807-12. doi: 10.1038/hr.2015.84. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Hypertens Res. 2015. PMID: 26178154
-
D1-like receptors inhibit insulin-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation via down-regulation of insulin receptor expression.J Hypertens. 2009 May;27(5):1033-41. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283293c7b. J Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19293728 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine d(1)-like receptors suppress proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cell induced by insulin-like growth factor-1.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2014;36(3):140-7. doi: 10.3109/10641963.2013.789048. Epub 2013 May 28. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 23713966
-
Dopamine D1 receptor augmentation of D3 receptor action in rat aortic or mesenteric vascular smooth muscles.Hypertension. 2004 Mar;43(3):673-9. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000118958.27649.6f. Epub 2004 Feb 9. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 14769810
-
Aberrant D1 and D3 dopamine receptor transregulation in hypertension.Hypertension. 2004 Mar;43(3):654-60. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000114601.30306.bf. Epub 2004 Jan 19. Hypertension. 2004. PMID: 14732731
Cited by
-
Dopamine and renal function and blood pressure regulation.Compr Physiol. 2011 Jul;1(3):1075-117. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c100032. Compr Physiol. 2011. PMID: 23733636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Sequencing and Pathway Analysis Identify Important Pathways Involved in Hypertrichosis and Intellectual Disability in Patients with Wiedemann-Steiner Syndrome.Neuromolecular Med. 2018 Sep;20(3):409-417. doi: 10.1007/s12017-018-8502-1. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Neuromolecular Med. 2018. PMID: 30014449
-
The association between index-year, average, and variability of the triglyceride-glucose index with health outcomes: more than a decade of follow-up in Tehran lipid and glucose study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Aug 31;23(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02387-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39217401 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of D1-like dopamine receptors on neuropeptide Y-induced proliferation in vascular smooth muscle cells.Hypertens Res. 2015 Dec;38(12):807-12. doi: 10.1038/hr.2015.84. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Hypertens Res. 2015. PMID: 26178154
-
Gastrin and D1 dopamine receptor interact to induce natriuresis and diuresis.Hypertension. 2013 Nov;62(5):927-33. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.113.01094. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 24019399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen TR, Krueger KD, Hunter WJ, 3rd, Agrawal DK. Evidence that insulin-like growth factor-1 requires protein kinase C-epsilon, PI3-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways to protect human vascular smooth muscle cells from apoptosis. Immunol Cell Biol. 2005;83:651–667. - PubMed
-
- Amenta F, Ricci A, Tayebati SK, Zaccheo D. The peripheral dopaminergic system: morphological analysis, functional and clinical applications. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002;107:145–167. - PubMed
-
- An JJ, Cho SR, Jeong DW, Park KW, Ahn YS, Baik JH. Antiproliferative effects and cell death mediated by two isoforms of dopamine D2 receptors in pituitary tumor cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2003;206:49–62. - PubMed
-
- Banday AA, Lokhandwala MF. Oxidative stress reduces renal dopamine D1 receptor-Gq/11alpha G protein-phospholipase C signaling involving G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;293:F306–F315. - PubMed
-
- Bleeke T, Zhang H, Madamanchi N, Patterson C, Faber JE. Cate-cholamine-induced vascular wall growth is dependent on generation of reactive oxygen species. Circ Res. 2004;94:37–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

