Beta-adrenergic receptor activation during distinct patterns of stimulation critically modulates the PKA-dependence of LTP in the mouse hippocampus
- PMID: 18441285
- PMCID: PMC2364601
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.829208
Beta-adrenergic receptor activation during distinct patterns of stimulation critically modulates the PKA-dependence of LTP in the mouse hippocampus
Abstract
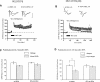
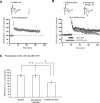
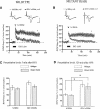
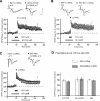
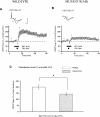
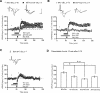
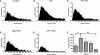
Activation of beta-adrenergic receptors (beta-ARs) enhances hippocampal memory consolidation and long-term potentiation (LTP), a likely mechanism for memory storage. One signaling pathway linked to beta-AR activation is the cAMP-PKA pathway. PKA is critical for the consolidation of hippocampal long-term memory and for the expression of some forms of long-lasting hippocampal LTP. How does beta-AR activation affect the PKA-dependence, and persistence, of LTP elicited by distinct stimulation frequencies? Here, we use in vitro electrophysiology to show that patterns of stimulation determine the temporal phase of LTP affected by beta-AR activation. In addition, only specific patterns of stimulation recruit PKA-dependent LTP following beta-AR activation. Impairments of PKA-dependent LTP maintenance generated by pharmacologic or genetic deficiency of PKA activity are also abolished by concurrent activation of beta-ARs. Taken together, our data show that, depending on patterns of synaptic stimulation, activation of beta-ARs can gate the PKA-dependence and persistence of synaptic plasticity. We suggest that this may allow neuromodulatory receptors to fine-tune neural information processing to meet the demands imposed by numerous synaptic activity profiles. This is a form of "metaplasticity" that could control the efficacy of consolidation of hippocampal long-term memories.
Figures
Similar articles
-
'Silent' priming of translation-dependent LTP by ß-adrenergic receptors involves phosphorylation and recruitment of AMPA receptors.Learn Mem. 2010 Nov 23;17(12):627-38. doi: 10.1101/lm.1974510. Print 2010 Dec. Learn Mem. 2010. PMID: 21097606 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term potentiation that is elicited by perforant path stimulation or that occurs in conjunction with spatial learning is tightly controlled by beta-adrenoreceptors and the locus coeruleus.Hippocampus. 2015 Nov;25(11):1285-98. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22436. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Hippocampus. 2015. PMID: 25727388 Free PMC article.
-
Noradrenergic stabilization of heterosynaptic LTP requires activation of Epac in the hippocampus.Learn Mem. 2019 Jan 16;26(2):31-38. doi: 10.1101/lm.048660.118. Print 2019 Feb. Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 30651375 Free PMC article.
-
Viagra for your synapses: Enhancement of hippocampal long-term potentiation by activation of beta-adrenergic receptors.Cell Signal. 2010 May;22(5):728-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.12.004. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20043991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of hippocampal synaptic plasticity by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases.Prog Neurobiol. 2003 Dec;71(6):401-37. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2003.12.003. Prog Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 15013227 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-Induced Enhanced Long-Term Potentiation and Reduced Threshold for N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor- and β-Adrenergic Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Plasticity in Rodent Ventral Subiculum.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Apr 22;14:658465. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.658465. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33967694 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-induced enhancement of mouse amygdalar synaptic plasticity depends on glucocorticoid and ß-adrenergic activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042143. Epub 2012 Aug 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22900007 Free PMC article.
-
Norepinephrine ignites local hotspots of neuronal excitation: How arousal amplifies selectivity in perception and memory.Behav Brain Sci. 2016 Jan;39:e200. doi: 10.1017/S0140525X15000667. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Behav Brain Sci. 2016. PMID: 26126507 Free PMC article.
-
β-Adrenoceptors and synaptic plasticity in the perirhinal cortex.Neuroscience. 2014 Jul 25;273(100):163-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.04.070. Epub 2014 May 14. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24836853 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of β-noradrenergic receptors enhances rhythmic bursting in mouse olfactory bulb external tufted cells.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Dec 1;116(6):2604-2614. doi: 10.1152/jn.00034.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 14. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 27628203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T., Lattal K.M. Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation, and retrieval. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2001;11:180–187. - PubMed
-
- Abel T., Nguyen P.V., Barad M., Deuel T.A., Kandel E.R., Bourtchouladze R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell. 1997;88:615–626. - PubMed
-
- Beebe S.J. The cAMP-dependent protein kinases and cAMP signal transduction. Semin. Cancer Biol. 1994;5:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Berridge C.W., Waterhouse B.D. The locus coeruleus-noradrenergic system: Modulation of behavioral state and state-dependent cognitive processes. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2003;42:33–84. - PubMed
-
- Bliss T.V., Collingridge G.L. A synaptic model of memory: Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
