Role of L-type Ca2+ channel isoforms in the extinction of conditioned fear
- PMID: 18441296
- PMCID: PMC2364608
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.886208
Role of L-type Ca2+ channel isoforms in the extinction of conditioned fear
Abstract
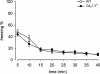
Dihydropyridine (DHP) L-type Ca(2+) channel (LTCC) antagonists, such as nifedipine, have been reported to impair the extinction of conditioned fear without interfering with its acquisition. Identification of the LTCC isoforms mediating this DHP effect is an essential basis to reveal their role as potential drug targets for the treatment of specific anxiety disorders. Ca(V)1.2 and Ca(V)1.3 are the predominant LTCCs in the mammalian brain. However, since no isoform-selective DHP blockers are available, their individual contribution to fear memory extinction is unknown. We used a novel mouse model expressing DHP-insensitive Ca(V)1.2 LTCCs (Ca(V)1.2DHP(-/-) mice) to address this question. In line with previous studies, wild-type (WT) mice treated with systemic nifedipine displayed markedly impaired fear extinction. This DHP effect was completely abolished in Ca(V)1.2DHP(-/-) mice, indicating that it is mediated by Ca(V)1.2, but not by Ca(V)1.3 LTCCs. Supporting this conclusion, Ca(V)1.3-deficient mice (Ca(V)1.3(-/-)) showed extinction identical to the respective WT mice. The inhibition of fear extinction was not observed after intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) application of different doses of nifedipine, suggesting that this effect is secondary to inhibition of peripheral Ca(V)1.2 channels. The LTCC activator BayK, which lacks neurotoxic effects in Ca(V)1.2DHP(-/-) mice, did not influence the extinction time course. In summary, we demonstrate that LTCC signaling through the Ca(V)1.2 isoform of LTCCs interferes with fear memory extinction, presumably via a peripherally mediated mechanism. Activation of other LTCC isoforms (predominantly Ca(V)1.3) is not sufficient to accelerate extinction of conditioned fear in mice.
Figures
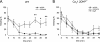
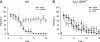
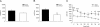
References
-
- Baker J.D., Azorlosa J.L. The NMDA antagonist MK-801 blocks the extinction of Pavlovian fear conditioning. Behav. Neurosci. 1996;110:618–620. - PubMed
-
- Barrett R.J., Wright K.F., Taylor D.R., Proakis A.G. Cardiovascular and renal actions of calcium channel blocker chemical subgroups: A search for renal specificity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1988;40:408–414. - PubMed
-
- Blair H.T., Schafe G.E., Bauer E.P., Rodrigues S.M., LeDoux J.E. Synaptic plasticity in the lateral amygdala: A cellular hypothesis of fear conditioning. Learn. Mem. 2001;8:229–242. - PubMed
-
- Bouton M.E. Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: Sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol. Psychiatry. 2002;52:976–986. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
