Entry to "formula tunnel" revealed by SLC4A4 human mutation and structural model
- PMID: 18441326
- PMCID: PMC2440602
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M709819200
Entry to "formula tunnel" revealed by SLC4A4 human mutation and structural model
Abstract
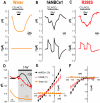
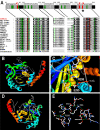
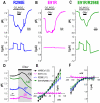
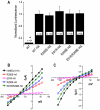
Glaucoma, cataracts, and proximal renal tubular acidosis are diseases caused by point mutations in the human electrogenic Na(+) bicarbonate cotransporter (NBCe1/SLC4A4) (1, 2). One such mutation, R298S, is located in the cytoplasmic N-terminal domain of NBCe1 and has only moderate (75%) function. As SLC transporters have high similarity in their membrane and N-terminal primary sequences, we homology-modeled NBCe1 onto the crystal structure coordinates of Band 3(AE1) (3). Arg-298 is predicted to be located in a solvent-inaccessible subsurface pocket and to associate with Glu-91 or Glu-295 via H-bonding and charge-charge interactions. We perturbed these putative interactions between Glu-91 and Arg-298 by site-directed mutagenesis and used expression in Xenopus oocyte to test our structural model. Mutagenesis of either residue resulted in reduced transport function. Function was "repaired" by charge reversal (E91R/R298E), implying that these two residues are interchangeable and interdependent. These results contrast the current understanding of the AE1 N terminus as protein-binding sites and propose that hkNBCe1 (and other SLC4) cytoplasmic N termini play roles in controlling HCO(3)(-) permeation.
Figures
References
-
- Igarashi, T., Inatomi, J., Sekine, T., Cha, S. H., Kanai, Y., Kunimi, M., Tsukamoto, K., Satoh, H., Shimadzu, M., Tozawa, F., Mori, T., Shiobara, M., Seki, G., and Endou, H. (1999) Nat. Genet. 23 264-266 - PubMed
-
- Romero, M. F., and Smith, B. L. (2002) FASEB J. 16 a52-a53
-
- Zhang, D., Kiyatkin, A., Bolin, J. T., and Low, P. S. (2000) Blood 96 2925-2933 - PubMed
-
- Alper, S. L. (2002) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64 899-923 - PubMed
-
- Romero, M. F. (2005) Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 14 495-501 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

