Effect of ezetimibe on the prevention and dissolution of cholesterol gallstones
- PMID: 18442485
- PMCID: PMC2741499
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.011
Effect of ezetimibe on the prevention and dissolution of cholesterol gallstones
Abstract
Background & aims: Cholesterol cholelithiasis is one of the most prevalent and most costly digestive diseases in developed countries and its incidence has increased markedly in Asian countries owing to the adoption of Western-type dietary habits. Because animal experiments showed that high efficiency of intestinal cholesterol absorption contributes to gallstone formation, we explored whether the potent cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe could prevent gallstones and promote gallstone dissolution in mice and reduce biliary cholesterol content in human beings.
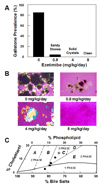
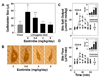
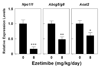
Methods: Male gallstone-susceptible C57L mice were fed a lithogenic diet and concomitantly administered with ezetimibe at 0, 0.8, 4, or 8 mg/kg/day for 8 or 12 weeks. Gallbladder biles and gallstones were examined by microscopy. Gallbladder emptying in response to cholecystokinin octapeptide was measured gravimetrically. Biliary lipid outputs were analyzed by physical-chemical methods. Cholesterol absorption efficiency was determined by fecal dual-isotope ratio and mass balance methods. Lipid changes in gallbladder biles of gallstone patients vs overweight subjects without gallstones were examined before (day 0) and at 30 days after ezetimibe treatment (20 mg/day).
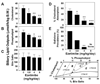
Results: Ezetimibe prevented gallstones by effectively reducing intestinal cholesterol absorption and biliary cholesterol secretion, and protected gallbladder motility function by desaturating bile in mice. Treatment with ezetimibe promoted the dissolution of gallstones by forming an abundance of unsaturated micelles. Furthermore, ezetimibe significantly reduced biliary cholesterol saturation and retarded cholesterol crystallization in biles of patients with gallstones.
Conclusions: Ezetimibe is a novel approach to reduce biliary cholesterol content and a promising strategy for preventing or treating cholesterol gallstones by inhibiting intestinal cholesterol absorption.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to disclose for all authors.
All authors do not have a financial or other affiliation with Merck/Schering-Plough.
Figures
References
-
- Wang DQ-H, Afdhal NH. Genetic analysis of cholesterol gallstone formation: searching for Lith (gallstone) genes. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2004;6:140–150. - PubMed
-
- Portincasa P, Moschetta A, Palasciano G. Cholesterol gallstone disease. Lancet. 2006;368:230–239. - PubMed
-
- Wang HH, Afdhal NH, Wang DQ-H. Overexpression of estrogen receptor α increases hepatic cholesterogenesis, leading to biliary hypersecretion in mice. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:778–786. - PubMed
-
- Turley SD, Dietschy JM. The contribution of newly synthesized cholesterol to biliary cholesterol in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:2438–2446. - PubMed
-
- Wang DQ-H, Zhang L, Wang HH. High cholesterol absorption efficiency and rapid biliary secretion of chylomicron remnant cholesterol enhance cholelithogenesis in gallstone-susceptible mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1733:90–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

