Cytokines link Toll-like receptor 4 signaling to cardiac dysfunction after global myocardial ischemia
- PMID: 18442564
- PMCID: PMC3137640
- DOI: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.01.043
Cytokines link Toll-like receptor 4 signaling to cardiac dysfunction after global myocardial ischemia
Abstract
Background: Although Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) has been implicated in the myocardial injury caused by regional ischemia/reperfusion, its role in the myocardial inflammatory response and in contractile dysfunction after global ischemia/reperfusion is unclear. Cytokines, particularly tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), contribute to the mechanism of myocardial dysfunction after global ischemia/reperfusion. We hypothesized that a TLR4-mediated cytokine cascade modulates myocardial contractile function after global ischemia/reperfusion. This study examined whether TLR4 regulates TNF-alpha and interleukin (IL)-1beta peptide production during global ischemia/reperfusion and whether TLR4 signaling influences postischemic cardiac function through TNF-alpha and IL-1beta.
Methods: Isolated hearts from wild-type mice, two strains of TLR4 mutants, TNF-alpha knockouts, and IL-1beta knockouts underwent global ischemia/reperfusion. Cardiac contractile function was analyzed, and myocardial nuclear factor-kappaB activity and TNF-alpha and IL-1beta levels were measured.
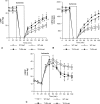
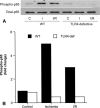
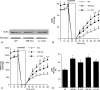
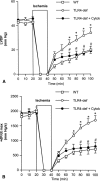
Results: In wild-type hearts, global ischemia/reperfusion induced nuclear factor-kappaB activation and the production of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta peptides. In TLR4-mutant hearts, these changes were significantly reduced and postischemic functional recovery was improved. Application of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta to TLR4-mutant hearts abrogated this improvement in postischemic functional recovery. Postischemic functional recovery also improved in TNF-alpha knockout and IL-1beta knockout hearts, as well as in wild-type hearts treated with TNF-binding protein or IL-1 receptor antagonist.
Conclusions: This study demonstrates that TLR4 signaling contributes to cardiac dysfunction after global ischemia/reperfusion. TLR4 signaling mediates the production of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta peptides, and these two cytokines link TLR4 signaling to postischemic cardiac dysfunction.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cytokines link Toll-like receptor 4 signaling to cardiac dysfunction after global myocardial ischemia. Invited commentary.Ann Thorac Surg. 2008 May;85(5):1685. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.02.091. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008. PMID: 18442565 No abstract available.
References
-
- Meldrum DR, Meng X, Dinarello CA, et al. Human myocardial tissue TNFα expression following acute global ischemia in vivo. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998;30:1683–9. - PubMed
-
- Cain BS, Meldrum DR, Dinarello CA, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta synergistically depress human myocardial function. Crit Care Med. 1999;27:1309–18. - PubMed
-
- Tomasdottir H, Hjartarson H, Ricksten A, Wasslavik C, Bengtsson A, Ricksten SE. Tumor necrosis factor gene polymorphism is associated with enhanced systemic inflammatory response and increased cardiopulmonary morbidity after cardiac surgery. Anesth Analg. 2003;97:944–9. - PubMed
-
- Meng X, Ao L, Song Y, Raeburn CD, Fullerton DA, Harken AH. Signaling for myocardial depression in hemorrhagic shock: roles of Toll-like receptor 4 and p55 TNF-alpha receptor. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288:R600–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhai Y, Shen XD, O'Connell R, et al. TLR4 activation mediates liver ischemia/reperfusion inflammatory response via IFN regulatory factor 3-dependent MyD88-independent pathway. J Immunol. 2004;173:7115–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

