Activation of 5-HT2A/C receptors counteracts 5-HT1A regulation of n-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex
- PMID: 18442977
- PMCID: PMC2427346
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801713200
Activation of 5-HT2A/C receptors counteracts 5-HT1A regulation of n-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex
Abstract
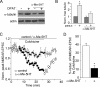
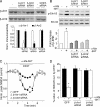
Abnormal serotonin-glutamate interaction in prefrontal cortex (PFC) is implicated in the pathophysiology of many mental disorders, including schizophrenia and depression. However, the mechanisms by which this interaction occurs remain unclear. Our previous study has shown that activation of 5-HT(1A) receptors inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor (NMDAR) currents in PFC pyramidal neurons by disrupting microtubule-based transport of NMDARs. Here we found that activation of 5-HT(2A/C) receptors significantly attenuated the effect of 5-HT(1A) on NMDAR currents and microtubule depolymerization. The counteractive effect of 5-HT(2A/C) on 5-HT(1A) regulation of synaptic NMDAR response was also observed in PFC pyramidal neurons from intact animals treated with various 5-HT-related drugs. Moreover, 5-HT(2A/C) stimulation triggered the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in dendritic processes. Inhibition of the beta-arrestin/Src/dynamin signaling blocked 5-HT(2A/C) activation of ERK and the counteractive effect of 5-HT(2A/C) on 5-HT(1A) regulation of NMDAR currents. Immunocytochemical studies showed that 5-HT(2A/C) treatment blocked the inhibitory effect of 5-HT(1A) on surface NR2B clusters on dendrites, which was prevented by cellular knockdown of beta-arrestins. Taken together, our study suggests that serotonin, via 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(2A/C) receptor activation, regulates NMDAR functions in PFC neurons in a counteractive manner. 5-HT(2A/C), by activating ERK via the beta-arrestin-dependent pathway, opposes the 5-HT(1A) disruption of microtubule stability and NMDAR transport. These findings provide a framework for understanding the complex interactions between serotonin and NMDARs in PFC, which could be important for cognitive and emotional control in which both systems are highly involved.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors regulate NMDA receptor channels through a microtubule-dependent mechanism.J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 8;25(23):5488-501. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1187-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15944377 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neuronal excitability by serotonin-NMDA interactions in prefrontal cortex.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008 Jun;38(2):290-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2008.03.003. Epub 2008 Mar 25. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18455431 Free PMC article.
-
Clozapine functions through the prefrontal cortex serotonin 1A receptor to heighten neuronal activity via calmodulin kinase II-NMDA receptor interactions.J Neurochem. 2012 Feb;120(3):396-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07565.x. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22044428 Free PMC article.
-
[Serotonergic control of prefrontal cortex].Rev Neurol. 2004 Sep 16-30;39(6):539-47. Rev Neurol. 2004. PMID: 15467993 Review. Spanish.
-
Serotonergic regulation of neuronal excitability in the prefrontal cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2011 Sep;61(3):382-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.015. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21251917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cortical plasticity, excitatory-inhibitory balance, and sensory perception.Prog Brain Res. 2013;207:65-90. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63327-9.00003-5. Prog Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 24309251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fenfluramine diminishes NMDA receptor-mediated seizures via its mixed activity at serotonin 5HT2A and type 1 sigma receptors.Oncotarget. 2018 May 4;9(34):23373-23389. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25169. eCollection 2018 May 4. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29805740 Free PMC article.
-
Activity-dependent serotonergic excitation of callosal projection neurons in the mouse prefrontal cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Aug 26;8:97. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00097. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 25206322 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic innervation and serotonin receptor expression of NPY-producing neurons in the rat lateral and basolateral amygdaloid nuclei.Brain Struct Funct. 2013 Mar;218(2):421-35. doi: 10.1007/s00429-012-0406-5. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Brain Struct Funct. 2013. PMID: 22527118 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin receptor signaling and regulation via β-arrestins.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Dec;45(6):555-66. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2010.516741. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20925600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buhot, M. C. (1997) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 7 243–254 - PubMed
-
- Andrade, R. (1998) Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 861 190–203 - PubMed
-
- Martin, G. R., Eglen, R. M., Hamblin, M. W., Hoyer, D., and Yocca, F. (1998) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19 2–4 - PubMed
-
- Gross, C., Zhuang, X., Stark, K., Ramboz, S., Oosting, R., Kirby, L., Santarelli, L., Beck, S., and Hen, R. (2002) Nature 416 396–400 - PubMed
-
- Saudou, F., Amara, D. A., Dierich, A., LeMeur, M., Ramboz, S., Segu, L., Buhot, M. C., and Hen, R. (1994) Science 265 1875–1878 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

