A locking mechanism regulates RNA synthesis and host protein interaction by the hepatitis C virus polymerase
- PMID: 18442978
- PMCID: PMC2459299
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801490200
A locking mechanism regulates RNA synthesis and host protein interaction by the hepatitis C virus polymerase
Abstract
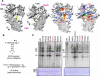
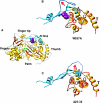
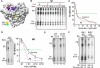
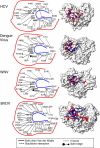
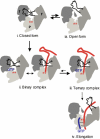
Mutational analysis of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) template channel identified two residues, Trp(397) and His(428), which are required for de novo initiation but not for extension from a primer. These two residues interact with the Delta1 loop on the surface of the RdRp. A deletion within the Delta1 loop also resulted in comparable activities. The mutant proteins exhibit increased double-stranded RNA binding compared with the wild type, suggesting that the Delta1 loop serves as a flexible locking mechanism to regulate the conformations needed for de novo initiation and for elongative RNA synthesis. A similar locking motif can be found in other viral RdRps. Products associated with the open conformation of the HCV RdRp were inhibited by interaction with the retinoblastoma protein but not cyclophilin A. Different conformations of the HCV RdRp can thus affect RNA synthesis and interaction with cellular proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Regulation of de novo-initiated RNA synthesis in hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by intermolecular interactions.J Virol. 2010 Jun;84(12):5923-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02446-09. Epub 2010 Apr 7. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 20375156 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of fingers subdomain-specific monoclonal antibodies inhibiting the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.J Biol Chem. 2008 Aug 29;283(35):24089-102. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803422200. Epub 2008 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18574240 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and functional characterization of the nascent RNA contacting residues of the hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.RNA. 2012 Aug;18(8):1541-52. doi: 10.1261/rna.031914.111. Epub 2012 Jun 26. RNA. 2012. PMID: 22736798 Free PMC article.
-
RNA synthetic mechanisms employed by diverse families of RNA viruses.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013 Jul-Aug;4(4):351-67. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1164. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2013. PMID: 23606593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ins and outs of four-tunneled Reoviridae RNA-dependent RNA polymerases.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Dec;19(6):775-82. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Nov 14. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19914820 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Akt Phosphorylation of Hepatitis C Virus NS5B Regulates Polymerase Activity and Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 22;12:754664. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.754664. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34745059 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and regulatory elements of HCV NS5B polymerase--β-loop and C-terminal tail--are required for activity of allosteric thumb site II inhibitors.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 9;9(1):e84808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084808. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416288 Free PMC article.
-
NMR reveals the intrinsically disordered domain 2 of NS5A protein as an allosteric regulator of the hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase NS5B.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 3;292(44):18024-18043. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.813766. Epub 2017 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28912275 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical study of the comparative inhibition of hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase by VX-222 and filibuvir.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Feb;56(2):830-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05438-11. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22143520 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric inhibitors have distinct effects, but also common modes of action, in the HCV polymerase.Biophys J. 2015 Apr 7;108(7):1785-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.005. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25863069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steitz, T. A. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274 17395-17398 - PubMed
-
- Lesburg, C. A., Cable, M. B., Ferrari, E., Hong, Z., Mannarino, A. F., and Weber, P. C. (1999) Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 937-943 - PubMed
-
- Butcher, S. J., Grimes, J. M., Makeyev, E. V., Bramford, D. H., and Stuart, D. I. (2001) Nature 410 235-240 - PubMed
-
- Hansen, J. L., Long, A. M., and Schultz, S. C. (1997) Structure 5 1109-1122 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

