Anemia and splenomegaly in cGKI-deficient mice
- PMID: 18443297
- PMCID: PMC2373362
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708940105
Anemia and splenomegaly in cGKI-deficient mice
Abstract
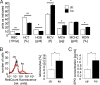
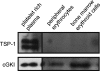
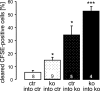
To explore the functional significance of cGMP-dependent protein kinase type I (cGKI) in the regulation of erythrocyte survival, gene-targeted mice lacking cGKI were compared with their control littermates. By the age of 10 weeks, cGKI-deficient mice exhibited pronounced anemia and splenomegaly. Compared with control mice, the cGKI mutants had significantly lower red blood cell count, packed cell volume, and hemoglobin concentration. Anemia was associated with a higher reticulocyte number and an increase of plasma erythropoietin concentration. The spleens of cGKI mutant mice were massively enlarged and contained a higher fraction of Ter119(+) erythroid cells, whereas the relative proportion of leukocyte subpopulations was not changed. The Ter119(+) cGKI-deficient splenocytes showed a marked increase in annexin V binding, pointing to phosphatidylserine (PS) exposure at the outer membrane leaflet, a hallmark of suicidal erythrocyte death or eryptosis. Compared with control erythrocytes, cGKI-deficient erythrocytes exhibited in vitro a higher cytosolic Ca(2+) concentration, a known trigger of eryptosis, and showed increased PS exposure, which was paralleled by a faster clearance in vivo. Together, these results identify a role of cGKI as mediator of erythrocyte survival and extend the emerging concept that cGMP/cGKI signaling has an antiapoptotic/prosurvival function in a number of cell types in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Dimmeler S, Haendeler J, Zeiher AM. Regulation of endothelial cell apoptosis in atherothrombosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2002;13:531–536. - PubMed
-
- Liu L, Stamler JS. NO: an inhibitor of cell death. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6:937–942. - PubMed
-
- Brune B. NO apoptosis or turning it ON? Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:864–869. - PubMed
-
- Nagai-Kusuhara A, et al. cAMP-responsive element binding protein mediates a cGMP/protein kinase G-dependent anti-apoptotic signal induced by nitric oxide in retinal neuro-glial progenitor cells. Exp Eye Res. 2007;84:152–162. - PubMed
-
- Friebe A, Koesling D. Regulation of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase. Circ Res. 2003;93:96–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

