Antiangiogenic and anticolorectal cancer effects of metronomic irinotecan chemotherapy alone and in combination with semaxinib
- PMID: 18443598
- PMCID: PMC2391121
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604352
Antiangiogenic and anticolorectal cancer effects of metronomic irinotecan chemotherapy alone and in combination with semaxinib
Abstract
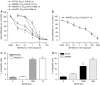
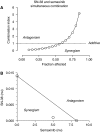
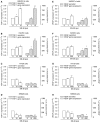
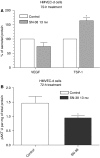
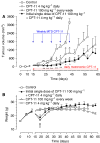
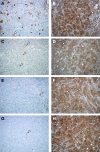
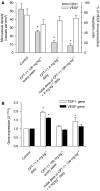
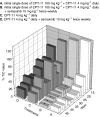
Metronomic chemotherapy refers to the administration of chemotherapy at low, nontoxic doses on a frequent schedule with no prolonged breaks. The aim of the study is to rationally develop a CPT-11 metronomic regimen in preclinical settings of colon cancer. In vitro cell proliferation, apoptosis and thrombospondin-1/vascular endothelial growth factor (TSP-1/VEGF) expression analyses were performed on endothelial (HUVEC, HMVEC-d) and colorectal cancer (HT-29, SW620) cells exposed for 144 h to metronomic concentrations of SN-38, the active metabolite of CPT-11. HT-29 human colorectal cancer xenograft model was used, and tumour growth, microvessel density and VEGF/TSP-1 quantification was performed in tumours. In vitro and in vivo combination studies with the tyrosine inhibitor semaxinib were also performed. SN-38 preferentially inhibited endothelial cell proliferation alone and interacted synergistically with semaxinib; it induced apoptosis and increased the expression and secretion of TSP-1. Metronomic CPT-11 alone and combined with semaxinib significantly inhibits tumour growth in the absence of toxicity, which was accompanied by decreases in microvessel density and increases in TSP-1 gene expression in tumour tissues. In vitro results show the antiangiogenic properties of low-concentration SN-38, suggesting a key role of TSP-1 in this effect. In vivo, the CPT-11 metronomic schedule is effective against tumour and microvessel growth without toxic effect on mice.
Figures
References
-
- Allegrini G, Goulette FA, Darnowski JW, Calabresi P (2004) Thrombospondin-1 plus irinotecan: a novel antiangiogenic–chemotherapeutic combination that inhibits the growth of advanced human colon tumor xenografts in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 53: 261–266 - PubMed
-
- Bertolini F, Paul S, Mancuso P, Monestiroli S, Gobbi A, Shaked Y, Kerbel RS (2003) Maximum tolerable dose and low-dose metronomic chemotherapy have opposite effects on the mobilization and viability of circulating endothelial progenitor cells. Cancer Res 63: 4342–4346 - PubMed
-
- Bocci G, Danesi R, Marangoni G, Fioravanti A, Boggi U, Esposito I, Fasciani A, Boschi E, Campani D, Bevilacqua G, Mosca F, Del Tacca M (2004a) Antiangiogenic vs cytotoxic therapeutic approaches to human pancreas cancer: an experimental study with a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor and gemcitabine. Eur J Pharmacol 498: 9–18 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

