Antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX: 12-month results of a prospective multicenter study
- PMID: 18443855
- PMCID: PMC2490723
- DOI: 10.1007/s00268-008-9594-9
Antireflux transoral incisionless fundoplication using EsophyX: 12-month results of a prospective multicenter study
Abstract
Background: A novel transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) procedure using the EsophyX system with SerosaFuse fasteners was designed to reconstruct a full-thickness valve at the gastroesophageal junction through tailored delivery of multiple fasteners during a single-device insertion. The safety and efficacy of TIF for treating gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) were evaluated in a prospective multicenter trial.
Methods: Patients (n = 86) with chronic GERD treated with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) were enrolled. Exclusion criteria included an irreducible hiatal hernia > 2 cm.
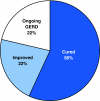
Results: The TIF procedure (n = 84) reduced all hiatal hernias (n = 49) and constructed valves measuring 4 cm (2-6 cm) and 230 degrees (160 degrees -300 degrees ). Serious adverse events consisted of two esophageal perforations upon device insertion and one case of postoperative intraluminal bleeding. Other adverse events were mild and transient. At 12 months, aggregate (n = 79) and stratified Hill grade I tight (n = 21) results showed 73% and 86% of patients with >or=50% improvement in GERD health-related quality of life (HRQL) scores, 85% discontinuation of daily PPI use, and 81% complete cessation of PPIs; 37% and 48% normalization of esophageal acid exposure; 60% and 89% hiatal hernia reduction; and 62% and 80% esophagitis reduction, respectively. More than 50% of patients with Hill grade I tight valves had a normalized cardia circumference. Resting pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) was improved significantly (p < 0.001), by 53%. EsophyX-TIF cured GERD in 56% of patients based on their symptom reduction and PPI discontinuation.
Conclusion: The 12-month results showed that EsophyX-TIF was safe and effective in improving quality of life and for reducing symptoms, PPI use, hiatal hernia, and esophagitis, as well as increasing the LES resting pressure and normalizing esophageal pH and cardia circumference in chronic GERD patients.
Figures




Comment in
-
Endoscopic antireflux surgery: are we there yet?World J Surg. 2008 Aug;32(8):1578-80. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9603-z. World J Surg. 2008. PMID: 18427888 No abstract available.
References
-
- Metz DC. Managing gastroesophageal reflux disease for the lifetime of the patient: evaluating the long-term options. Am J Med. 2004;117( Suppl 5A):49S–55S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

