Prevalence and risk factors of maladaptive behaviour in young children with Autistic Disorder
- PMID: 18444989
- PMCID: PMC2838711
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2008.01065.x
Prevalence and risk factors of maladaptive behaviour in young children with Autistic Disorder
Abstract
Background: Children with Autistic Disorder (AD) evidence more co-occurring maladaptive behaviours than their typically developing peers and peers with intellectual disability because of other aetiologies. The present study investigated the prevalence of Clinically Significant maladaptive behaviours during early childhood and identified at-risk subgroups of young children with AD.
Method: Parents rated their child's maladaptive behaviours on the Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) in 169 children with AD aged 1.5 to 5.8 years.
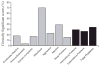
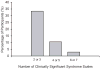
Results: One-third of young children with AD had a CBCL Total Problems score in the Clinically Significant range. The highest percentage of Clinically Significant scores were in the Withdrawal, Attention, and Aggression CBCL syndrome scales. There was a high degree of co-morbidity of Clinically Significant maladaptive behaviours. Several subject characteristic risk factors for maladaptive behaviours were identified.
Conclusions: Findings highlight the need to include behavioural management strategies aimed at increasing social engagement, sustained attention and decreasing aggressive behaviour in comprehensive intervention programmes for young children with AD.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach T, Rescorla L. Child Behavior Checklist. ASEBA; Burlington, VT: 2000.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. American Psychiatric Association Press; Washington, D.C: 2000. Text Revision.
-
- Bolte S, Dickhut H, Poustka F. Patterns of parent-rated problems indicative of autism. Psychopathology. 1999;32:93–7. - PubMed
-
- Bradley EA, Summers JA, Wood HL, Bryson SE. Comparing rates of psychiatric and behavior disorders in adolescents and young adults with severe intellectual disability with and without autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2004;34:151–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical