TNF-alpha-induced up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is regulated by a Rac-ROS-dependent cascade in human airway epithelial cells
- PMID: 18446055
- PMCID: PMC2679306
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.2.167
TNF-alpha-induced up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is regulated by a Rac-ROS-dependent cascade in human airway epithelial cells
Abstract
Up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the lung airway epithelium is associated with the epithelium-leukocyte interaction, critical for the pathogenesis of various lung airway inflammatory diseases such as asthma. However, little is known about how ICAM-1 is up-regulated in human airway epithelial cells. In this study, we show that tumor TNF-alpha induces monocyte adhesion to A549 human lung airway epithelium and also up-regulation of ICAM-1 expression. These effects were significantly diminished by pre-treatment with diphenyliodonium (DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase-like flavoenzyme. In addition, the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was increased in response to TNF-alpha in A549 cells, suggesting a potential role of ROS in the TNF-alpha-induced signaling to ICAM-1 expression and monocyte adhesion to airway epithelium. Further, we found out that expression of RacN17, a dominant negative mutant of Rac1, suppressed TNF-alpha-induced ROS generation, ICAM-1 expression, and monocyte adhesion to airway epithelium. These findings suggest that Rac1 lies upstream of ROS generation in the TNF-alpha-induced signaling to ICAM-1 expression in airway epithelium. Finally, pretreatment with pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), an inhibitor of NF-kappaB, reduced TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 expression and both DPI and RacN17 significantly diminished NF-kappaB activation in response to TNF-alpha. Together, we propose that Rac1-ROS-linked cascade mediate TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 up-regulation in the airway epithelium via NF-kappaB-dependent manner.
Figures





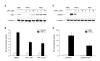
References
-
- Adachi T, Togashi H, Suzuki A, Kasai S, Ito J, Sugahara K, Kawata S. NAD(P)H oxidase plays a crucial role in PDGF-induced proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2005;41:1272–1281. - PubMed
-
- Akasaki T, Koga H, Sumimoto H. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase-dependent and -independent activation of the small GTPase Rac2 in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18055–18059. - PubMed
-
- Chung JW, Kim GY, Mun YC, Ahn JY, Seong CM, Kim JH. Leukotriene B4 pathway regulates the fate of the hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Mol Med. 2005;37:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Colavitti R, Pani G, Bedogni B, Anzevino R, Borrello S, Waltenberger J, Galeotti T. Reactive oxygen species as downstream mediators of angiogenic signaling by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/KDR. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:3101–3108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
