Secretion of adenylate kinase 1 is required for extracellular ATP synthesis in C2C12 myotubes
- PMID: 18446060
- PMCID: PMC2679308
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.2.220
Secretion of adenylate kinase 1 is required for extracellular ATP synthesis in C2C12 myotubes
Abstract
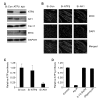
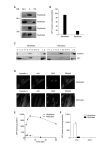
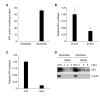
Extracellular ATP (exATP) has been known to be a critical ligand regulating skeletal muscle differentiation and contractibility. ExATP synthesis was greatly increased with the high level of adenylate kinase 1 (AK1) and ATP synthase beta during C2C12 myogenesis. The exATP synthesis was abolished by the knock-down of AK1 but not by that of ATP synthase beta in C2C12 myotubes, suggesting that AK1 is required for exATP synthesis in myotubes. However, membrane-bound AK1beta was not involved in exATP synthesis because its expression level was decreased during myogenesis in spite of its localization in the lipid rafts that contain various kinds of receptors and mediate cell signal transduction, cell migration, and differentiation. Interestingly, cytoplasmic AK1 was secreted from C2C12 myotubes but not from C2C12 myoblasts. Taken together all these data, we can conclude that AK1 secretion is required for the exATP generation in myotubes.
Figures
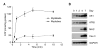
Similar articles
-
Defective metabolic signaling in adenylate kinase AK1 gene knock-out hearts compromises post-ischemic coronary reflow.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 26;282(43):31366-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705268200. Epub 2007 Aug 17. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17704060 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular characterization of adenylate kinase and its isoform: two-photon excitation fluorescence imaging and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy.Biophys J. 2002 Dec;83(6):3177-87. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(02)75320-4. Biophys J. 2002. PMID: 12496087 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired intracellular energetic communication in muscles from creatine kinase and adenylate kinase (M-CK/AK1) double knock-out mice.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 15;278(33):30441-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303150200. Epub 2003 May 1. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12730234
-
Evidence for in vivo synthesis of thiamin triphosphate by cytosolic adenylate kinase in chicken skeletal muscle.J Biochem. 1990 Aug;108(2):267-70. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123192. J Biochem. 1990. PMID: 2229026
-
The many isoforms of human adenylate kinases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;49:75-83. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.01.014. Epub 2014 Feb 2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24495878 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-metabolite association studies identify novel proteomic determinants of metabolite levels in human plasma.Cell Metab. 2023 Sep 5;35(9):1646-1660.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.07.012. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Cell Metab. 2023. PMID: 37582364 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial complex I deficiency enhances skeletal myogenesis but impairs insulin signaling through SIRT1 inactivation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 18;289(29):20012-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.560078. Epub 2014 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24895128 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism of circulating ADP in the bloodstream is mediated via integrated actions of soluble adenylate kinase-1 and NTPDase1/CD39 activities.FASEB J. 2012 Sep;26(9):3875-83. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-205658. Epub 2012 May 25. FASEB J. 2012. PMID: 22637533 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signalling in the musculoskeletal system.Purinergic Signal. 2013 Dec;9(4):541-72. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9381-4. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Purinergic Signal. 2013. PMID: 23943493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An unexpected biomaterial against SARS-CoV-2: Bio-polyphosphate blocks binding of the viral spike to the cell receptor.Mater Today (Kidlington). 2021 Dec;51:504-524. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2021.07.029. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2021. PMID: 34366696 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbracchio MP, Boeynaems JM, Barnard EA, Boyer JL, Kennedy C, Miras-Portugal MT, King BF, Gachet C, Jacobson KA, Weisman GA, Burnstock G. Characterization of the UDP-glucose receptor (re-named here the P2Y14 receptor) adds diversity to the P2Y receptor family. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2003;24:52–55. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arakaki N, Nagao T, Niki R, Toyofuku A, Tanaka H, Kuramoto Y, Emoto Y, Shibata H, Magota K, Higuti T. Possible role of cell surface H+-ATP synthase in the extracellular ATP synthesis and proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:931–939. - PubMed
-
- Araya R, Riquelme MA, Brandan E, Saez JC. The formation of skeletal muscle myotubes requires functional membrane receptors activated by extracellular ATP. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004;47:174–188. - PubMed
-
- Bae TJ, Kim MS, Kim JW, Kim BW, Choo HJ, Lee JW, Kim KB, Lee CS, Kim JH, Chang SY, Kang CY, Lee SW, Ko YG. Lipid raft proteome reveals ATP synthase complex in the cell surface. Proteomics. 2004;4:3536–3548. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
