Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy
- PMID: 18446337
- PMCID: PMC3401888
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0523-4
Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy
Abstract
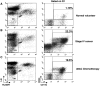
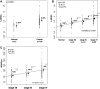
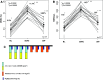
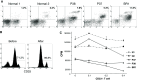
Abnormal accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC) is an important mechanism of tumor immune evasion. Cyclophosphamide (CTX) has also been shown in non-tumor bearing animals to cause transient surges in MDSC. Knowledge of MDSC is primarily based on preclinical work, and to date only few published studies have involved cancer patients. The goal of this study was to test the hypothesis that circulating MDSC levels correlate with clinical cancer stage, CTX-based chemotherapy, and metastatic tumor burden. Whole blood was collected from 106 newly diagnosed solid tumor patients (stages I-IV). Percentages of circulating MDSC (Lin(-/Lo), HLA DR-, CD33(+)CD11b(+)) were determined prior to initiation of systemic therapy. In 17 early stage breast cancer patients receiving doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy every 14 days (ddAC) blood was collected on day 1 of each cycle. Circulating MDSC were significantly increased in cancer patients of all stages relative to healthy volunteers. A significant correlation between circulating MDSC and clinical cancer stage was also observed. Moreover, among stage IV patients, those with extensive metastatic tumor burden had the highest percent and absolute number of MDSC. Significant increases in circulating MDSC were observed with ddAC when compared with pretreatment levels. Circulating MDSC levels correlate with clinical cancer stage, ddAC, and metastatic tumor burden. This information must be incorporated into the design of future trials exploring immune-based therapeutic strategies. Pharmacologic modulation of MDSC should also be tested in future clinical trials.
Figures


References
-
- Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, Carbone DP, Gabrilovich DI. Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol. 2001;166:678. - PubMed
-
- Almand B, Resser JR, Lindman B, Nadaf S, Clark JI, Kwon ED, Carbone DP, Gabrilovich DI. Clinical significance of defective dendritic cell differentiation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:1755. - PubMed
-
- Angulo I, de las Heras FG, Garcia-Bustos JF, Gargallo D, Munoz-Fernandez MA, Fresno M. Nitric oxide-producing CD11b(+) Ly-6G(Gr-1)(+) CD31(ER-MP12)(+) cells in the spleen of cyclophosphamide-treated mice: implications for T cell responses in immunosuppressed mice. Blood. 2000;95:212. - PubMed
-
- Brito C, Naviliat M, Tiscornia AC, Vuillier F, Gualco G, Dighiero G, Radi R, Cayota AM. Peroxynitrite inhibits T lymphocyte activation and proliferation by promoting impairment of tyrosine phosphorylation and peroxynitrite-driven apoptotic death. J Immunol. 1999;162:3356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

