Implementation of a semi-automated post-processing system for parametric MRI mapping of human breast cancer
- PMID: 18446412
- PMCID: PMC3043701
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-008-9123-2
Implementation of a semi-automated post-processing system for parametric MRI mapping of human breast cancer
Abstract
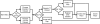
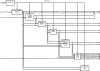
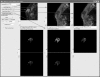
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) investigations of breast cancer incorporate computationally intense techniques to develop parametric maps of pathophysiological tissue characteristics. Common approaches employ, for example, quantitative measurements of T (1), the apparent diffusion coefficient, and kinetic modeling based on dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI). In this paper, an integrated medical image post-processing and archive system (MIPAS) is presented. MIPAS demonstrates how image post-processing and user interface programs, written in the interactive data language (IDL) programming language with data storage provided by a Microsoft Access database, and the file system can reduce turnaround time for creating MRI parametric maps and provide additional organization for clinical trials. The results of developing the MIPAS are discussed including potential limitations of the use of IDL for the application framework and how the MIPAS design supports extension to other programming languages and imaging modalities. We also show that network storage of images and metadata has a significant (p < 0.05) increase in data retrieval time compared to collocated storage. The system shows promise for becoming both a robust research picture archival and communications system working with the standard hospital PACS and an image post-processing environment that extends to other medical image modalities.
Figures





References
-
- Bollet MA, Thibault F, Bouillon K, Meunier M, Sigal-Zafrani B, Savignoni A, Diéras V, Nos C, Salmon R, Fourquet A, Institut Curie Breast Cancer Study Group Role of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of tumor response to preoperative concurrent radiochemotherapy for large breast cancers: a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;69:13–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

