Effect of Eudragit RS 30D and talc powder on verapamil hydrochloride release from beads coated with drug layered matrices
- PMID: 18446464
- PMCID: PMC2976883
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-007-9008-6
Effect of Eudragit RS 30D and talc powder on verapamil hydrochloride release from beads coated with drug layered matrices
Abstract
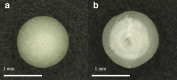
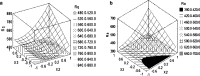
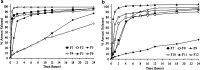
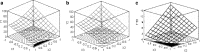
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of Eudragit RS 30D, talc, and verapamil hydrochloride on dissolution and mechanical properties of beads coated with "drug-layered matrices". This was accomplished with the aid of a three-factor multiple-level factorial design using percent drug release in 1 and 2 h, T(50), tensile strength, brittleness, stiffness and toughness as the responses. Beads were coated in a fluidized-bed coating unit. Surface morphology and mechanical properties were evaluated by surface profilometry and texture analysis, respectively. No cracks, flaws and fissures were observed on the surfaces. The mechanical properties were dependent on the talc/polymer ratio. The release of verapamil from the beads was influenced by matrix components. Increasing the level of both talc and Eudragit decreased the percent drug released from 67% to 4.8% and from 80.7% to 6.7% in 1 and 2 h, respectively, and increased T(50) from 0.8 to 25.7 h. It was concluded that beads could be efficiently coated with "drug-layered matrices". The release of drug, however, depends on a balance between the levels of drug, talc, and polymer, whereby desired dissolution and mechanical properties could be controlled by the talc/polymer ratio and the level of drug loading.
Figures

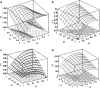
References
-
- T. Osawa, T. Takahata, H. Takahata, M. Maejima, M. Kbayashi, T. Noda. Sigmoidal releasing system (SRS) as a novel oral controlled release formulation. Proceedings of the Oral Controlled Release Formulation, 1991, pp 405–406.
-
- Follonier N., Doelker E. Biopharmaceutical comparison of oral multiple-unit and single unit sustained release dosage forms. S.T.P. Pharma Sci. 1992;2:141–158.
-
- Vaithiyalingam S., Reddy I. K., Khan M. A. Aquoeous-based cellulose acetate butyrate dispersion: Screening of process and formulation variables to obtain verapamil HCL-controlled release beads. Part. Sci. Tech. 2001;19:131–144. doi: 10.1080/02726350152772074. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

