Design and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of nimodipine
- PMID: 18446481
- PMCID: PMC2976914
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-008-9037-9
Design and evaluation of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) of nimodipine
Abstract
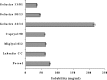
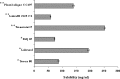
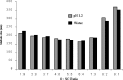
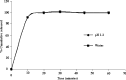
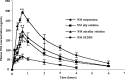
The ability of self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) to improve solubility, dissolution rate and bioavailability of a poorly water-soluble calcium channel blocker, nimodipine (NM) was evaluated in the present investigation. Solubility of NM in various oils, surfactants and cosurfactants was determined. The influence of the ratio of oil to surfactant + cosurfactant, pH of aqueous phase on mean globule size of resulting emulsions was studied by means of photon correlation spectroscopy. The NM loaded SEDDS selected for the in vitro and in vivo studies exhibited globule size less than 180 nm. In vitro dissolution studies indicated that NM loaded SEDDS could release complete amount of NM irrespective of the pH of the dissolution media. Pharmacokinetics of NM suspension, NM oily solution, NM micellar solution and NM SEDDS were evaluated and compared in rabbits. Relative bioavailability of NM in SEDDS was significantly higher than all the other formulations. NM loaded SEDDS were subjected to various conditions of storage as per ICH guidelines for 3 months. NM SEDDS successfully withstood the stability testing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of in vitro lipolysis for the development of oral self-emulsified delivery system of nimodipine.Int J Pharm. 2018 Dec 20;553(1-2):441-453. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.10.066. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Int J Pharm. 2018. PMID: 30385374
-
Insights into Novel Excipients of Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems and Their Significance: An Updated Review.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2021;38(2):27-74. doi: 10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2020034975. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2021. PMID: 33639067
-
Enhanced dissolution and oral absorption of tacrolimus by supersaturable self-emulsifying drug delivery system.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Mar 18;11:1109-17. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S102991. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27051286 Free PMC article.
-
Self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) for improved oral delivery of lipophilic drugs.Biomed Pharmacother. 2004 Apr;58(3):173-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2004.02.001. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15082340 Review.
-
Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery System Improve Oral Bioavailability: Role of Excipients and Physico-chemical Characterization.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(4):290-301. doi: 10.2174/2211738508666200811104240. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32781978 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced oral absorption of insulin: hydrophobic ion pairing and a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system using a D-optimal mixture design.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2831-2845. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2118399. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36050870 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dose and dosage interval on the oral bioavailability of docetaxel in combination with a curcumin self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS).Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012 Sep;37(3):217-24. doi: 10.1007/s13318-011-0078-1. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012. PMID: 22201019
-
3D printed multi-drug-loaded suppositories for acute severe ulcerative colitis.Int J Pharm X. 2023 Jan 29;5:100165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2023.100165. eCollection 2023 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2023. PMID: 36876053 Free PMC article.
-
Self-emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems: Concept to Applications, Regulatory Issues, Recent Patents, Current Challenges and Future Directions.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(3):341-364. doi: 10.2174/0113892010296223240612050639. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38910472 Review.
-
Improved oral bioavalability of mebudipine upon administration in PhytoSolve and Phosal-based formulation (PBF).AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Feb;15(1):96-102. doi: 10.1208/s12249-013-0039-x. Epub 2013 Oct 23. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014. PMID: 24151144 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang J. T. Altered calcium homeostasis in brain aging and senile dementia, new approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1993;28:641–646. - PubMed
-
- Pantoni L., Rossi R., Inzitari D., Bianchi C., Beneke M., Erkinjuntti T., Wallin T. Efficacy and safety of nimodipine in subcortical vascular dementia: a subgroup analysis of the Scandinavian Multi-Infarct Dementia Trial. J. Neurol. Sci. 2000;175:124–134. doi: 10.1016/S0022-510X(00)00300-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Muck W., Breuel H. P., Kuhlmann J. The influence of age on the pharmacokinetics of nimodipine. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996;34:293–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

