Intracellular delivery of nanoparticles of an antiasthmatic drug
- PMID: 18446484
- PMCID: PMC2976900
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-008-9036-x
Intracellular delivery of nanoparticles of an antiasthmatic drug
Abstract
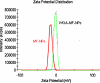
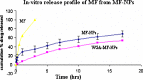
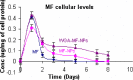
The aim of the investigation was to prepare and characterize wheat germ agglutinin(WGA)-conjugated poly(D: ,L-lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles encapsulating mometasone furoate (MF) as a model drug and assess changes in its fate in terms of cellular interactions. MF loaded nanoparticles were prepared using emulsion-solvent evaporation technique. WGA-conjugation was done by carbodiimide coupling method. The nanoparticles were characterized for size, zeta potential, entrapment efficiency and in-vitro drug release. The intracellular uptake of nanoparticles, drug cellular levels, and anti-proliferative activity studies of wheat germ agglutinin-conjugated and unconjugated nanoparticles were assessed on alveolar epithelial (A549) cells to establish cellular interactions. Prepared nanoparticles were spherical with 10-15 microg/mg of WGA conjugated on nanoparticles. The size of nanoparticles increased after conjugation and drug entrapment and zeta potential reduced from 78 +/- 5.5% to 60 +/- 2.5% and -15.3 +/- 1.9 to -2.59 +/- 2.1 mV respectively after conjugation. From the cellular drug concentration-time plot, AUC was found to be 0.4745, 0.6791 and 1.24 for MF, MF-nanoparticles and wheat germ agglutinin-MF-nanoparticles respectively. The in-vitro antiproliferative activity was improved and prolonged significantly after wheat germ agglutinin-conjugation. The results conclusively demonstrate improved availability and efficacy of antiasthmatic drug in alveolar epithelial cell lines. Hence, a drug once formulated as mucoadhesive nanoparticles and incorporated in dry powder inhaler formulation may be used for targeting any segment of lungs for more improved therapeutic response in other lung disorders as well.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

