Process analytical technology: application to particle sizing in spray drying
- PMID: 18446490
- PMCID: PMC2976913
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-007-9011-y
Process analytical technology: application to particle sizing in spray drying
Abstract
The purpose of this research was to explore the possibility of employing PAT for particle sizing during spray drying with the use of an in-line and at-line laser diffraction system. Microspheres were made using maltodextrin and modified starch as wall material and size results obtained using PAT compared with those determined with off-line laser diffraction and light microscopy. Median particle size results were highest for in-line laser diffraction, followed by at-line and off-line laser diffraction and finally light microscopy. This was due to the presence of agglomerates which were measured as discrete microspheres in the in-line set-up. At-line and off-line laser diffraction gave results more closely correlated with individual microsphere sizes due to agglomerate breakdown during the measurement process. Light microscopy allowed direct observation of the particle morphology, however, its use for particle sizing was tedious and sample size was much smaller compared to laser diffraction. Although PAT was found to be an efficient and convenient tool, careful data interpretation was needed taking into account the cohesiveness of the material measured. The at-line set-up appeared to be more suitable in this particular application.
Figures




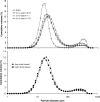
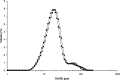
Similar articles
-
Presence of electrostatically adsorbed polysaccharides improves spray drying of liposomes.J Food Sci. 2013 Feb;78(2):E206-21. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12023. Epub 2013 Jan 16. J Food Sci. 2013. PMID: 23324113
-
Effect of oil droplet size on the oxidative stability of spray-dried flaxseed oil powders.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017 Apr;81(4):698-704. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2017.1281720. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28140765
-
Development of directly compressible powders via co-spray drying.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007 Aug;67(1):220-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2006.12.021. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007. PMID: 17317123
-
A new rapid on-line imaging method to determine particle size distribution of granules.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(1):282-7. doi: 10.1208/s12249-008-9043-y. Epub 2008 Feb 5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008. PMID: 18446493 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of particle sizing techniques in the case of inhalation dry powders.J Pharm Sci. 2001 Dec;90(12):2032-41. doi: 10.1002/jps.1154. J Pharm Sci. 2001. PMID: 11745762
Cited by
-
Combination of a rotating tube sample divider and dynamic image analysis for continuous on-line determination of granule size distribution.Int J Pharm X. 2019 Aug 12;1:100029. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2019.100029. eCollection 2019 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2019. PMID: 31517294 Free PMC article.
-
Solvent-free melting techniques for the preparation of lipid-based solid oral formulations.Pharm Res. 2015 May;32(5):1519-45. doi: 10.1007/s11095-015-1661-y. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25788447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide Isolation via Spray Drying: Particle Formation, Process Design and Implementation for the Production of Spray Dried Glucagon.Pharm Res. 2020 Dec 14;37(12):255. doi: 10.1007/s11095-020-02942-5. Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33319329 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of process parameters affecting spray-dried oily core nanocapsules using factorial design.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010 Sep;11(3):1422-31. doi: 10.1208/s12249-010-9516-7. Epub 2010 Sep 15. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010. PMID: 20839078 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of an inhalable DDA/TDB liposomal adjuvant: a quality-by-design approach towards optimization of the spray drying process.Pharm Res. 2013 Nov;30(11):2772-84. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-1096-2. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23794038
References
-
- Process Analytical Technology (PAT) Initiative. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration Website. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/cder/OPS/PAT.htm. Accessed December 7, 2005.
-
- Balboni M. L. Process analytical technology: Concepts and principles. Pharm. Technol. 2003;27(254):54–66.
-
- Brittain H. G. Physical characterization of pharmaceutical solids. New York: Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 1995. - PubMed
-
- Alderliesten M. Mean particle diameters. Part IV: Empirical selection of the proper type of mean particle diameter describing a product or material property. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2004;21:179–196. doi: 10.1002/ppsc.200400917. - DOI
-
- Allen T. Particle size measurement. Volume I. Powder sampling and particle size measurement. 5. London, UK: Chapman & Hall; 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

