A new rapid on-line imaging method to determine particle size distribution of granules
- PMID: 18446493
- PMCID: PMC2976888
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-008-9043-y
A new rapid on-line imaging method to determine particle size distribution of granules
Abstract
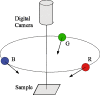
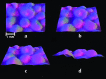
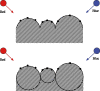
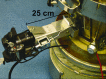
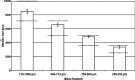
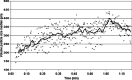
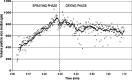
The purpose of this research was to study the feasibility of the new image analysis method in the particle size determination of the granules. The method is capable of forming a three-dimensional topographic image of a sample surface from a digital picture. In the method, a flat granule bed surface was illuminated from three different directions, using the three primary colors (red, green, and blue). One color picture was taken by a digital camera, after which a topographic image of the object surface was constructed. The particle size distribution was then calculated from the image data. The particle size analysis method was tested both off-line and on-line. Off-line particle size measurement results determined by the image analysis method corresponded quite well to those of sieve analysis in the size fraction range 250-1,000 microm. In on-line application, images were successfully retrieved and median granule size trend could be calculated and followed during fluid bed granulations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid particle size measurement using 3D surface imaging.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011 Jun;12(2):476-84. doi: 10.1208/s12249-011-9607-0. Epub 2011 Apr 9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011. PMID: 21479750 Free PMC article.
-
Process analytical technology: application to particle sizing in spray drying.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(1):259-66. doi: 10.1208/s12249-007-9011-y. Epub 2008 Jan 4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008. PMID: 18446490 Free PMC article.
-
Does a powder surface contain all necessary information for particle size distribution analysis?Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002 Dec;17(4-5):217-27. doi: 10.1016/s0928-0987(02)00189-6. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2002. PMID: 12453611
-
Colorful reconstructions from a thin multi-plane phase hologram.Opt Express. 2008 Jul 21;16(15):11618-23. Opt Express. 2008. PMID: 18648483
-
Ultrasound transmission technique as a potential tool for physical evaluation of monolithic matrix tablets.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(1):267-73. doi: 10.1208/s12249-007-9010-z. Epub 2008 Jan 9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008. PMID: 18446491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicting particle size during fluid bed granulation using process measurement data.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(4):1268-75. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9310-6. Epub 2009 Oct 30. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009. PMID: 19876742 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid particle size measurement using 3D surface imaging.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011 Jun;12(2):476-84. doi: 10.1208/s12249-011-9607-0. Epub 2011 Apr 9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011. PMID: 21479750 Free PMC article.
-
Particle size, moisture, and fluidization variations described by indirect in-line physical measurements of fluid bed granulation.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(4):1070-7. doi: 10.1208/s12249-008-9147-4. Epub 2008 Oct 17. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008. PMID: 18931917 Free PMC article.
-
The Future of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Sciences.J Pharm Sci. 2015 Nov;104(11):3612-3638. doi: 10.1002/jps.24594. Epub 2015 Aug 17. J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26280993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast tablet tensile strength prediction based on non-invasive analytics.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014 Jun;15(3):781-91. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0104-0. Epub 2014 Mar 18. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014. PMID: 24638870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Juslin L., Yliruusi J. Granule growth kinetics and attrition of granules made of different materials in a fluid bed granulator. STP Pharma. Sci. 1996;6:321–327.
-
- Rantanen J., Yliruusi J. Determination of particle size in a fluidized bed granulator with a near infrared set-up. Pharm. Pharmacol. Commun. 1998;4:73–75.
-
- Pasikatan M. C., Steele J. L., Spillman C. K., Haque E. Review: Near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for online particle size analysis of powders and ground materials. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2001;9:153–164.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

