Prodrug approaches for CNS delivery
- PMID: 18446509
- PMCID: PMC2751454
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-008-9009-8
Prodrug approaches for CNS delivery
Abstract
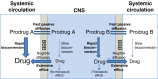
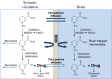
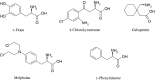
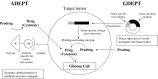
Central nervous system (CNS) drug delivery remains a major challenge, despite extensive efforts that have been made to develop novel strategies to overcome obstacles. Prodrugs are bioreversible derivatives of drug molecules that must undergo an enzymatic and/or chemical transformation in vivo to release the active parent drug, which subsequently exerts the desired pharmacological effect. In both drug discovery and drug development, prodrugs have become an established tool for improving physicochemical, biopharmaceutical or pharmacokinetic properties of pharmacologically active agents that overcome barriers to a drug's usefulness. This review provides insight into various prodrug strategies explored to date for CNS drug delivery, including lipophilic prodrugs, carrier- and receptor-mediated prodrug delivery systems, and gene-directed enzyme prodrug therapy.
Figures

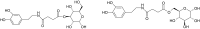
References
-
- Pardridge W. M. Why is the global CNS pharmaceutical market so under-penetrated. Drug Discov. Today. 2002;7(1):5–7. - PubMed
-
- Begley D. J. Delivery of therapeutic agents to the central nervous system: the problems and the possibilities. Pharmacol Ther. 2004;104(1):29–45. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury M. W. The structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Fed. Proc. 1984;43(2):186–190. - PubMed
-
- Janzer R. C., Raff M. C. Astrocytes induce blood–brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature. 1987;325(6101):253–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

