Nanoparticles containing anti-inflammatory agents as chemotherapy adjuvants: optimization and in vitro characterization
- PMID: 18446513
- PMCID: PMC2751458
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-008-9013-z
Nanoparticles containing anti-inflammatory agents as chemotherapy adjuvants: optimization and in vitro characterization
Abstract
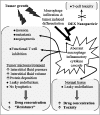
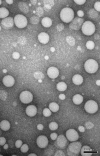
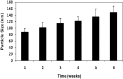
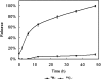
The pre-administration of dexamethasone (DEX) has previously been shown to enhance the anti-tumor efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents. The delivery of anti-inflammatory agents specifically to tumors via nanoparticle carriers is expected to promote the effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents while avoiding systemic toxicities. The process for preparing solid lipid nanoparticles containing anti-inflammatory agents using the nanotemplate engineering method was optimized. Due to the solubilization of DEX in the bulk aqueous phase, its more lipophilic palmitate ester was synthesized and incorporated in nanoparticles that included a pegylating agent, PEG6000 mono-stearate, as part of the formulation. The stealth properties of these nanoparticles were demonstrated to be enhanced compared to latex particles by measuring the adsorption of radioiodinated IgG (185 microg vs. 6.7 microg IgG/mg NP). In addition, the uptake of (14)C-labeled nanoparticles by murine macrophages was shown to decrease from 36.6% to 14.7% of the nanoparticles/mg cell protein as the amount of pegylating agent in the formulation increased from 0 to 4 mg/mL. The high loading values and low burst effect observed for these DEX palmitate-containing nanoparticles in addition to their stealth properties are expected to allow for the delivery of sufficient amounts of DEX to tumors to enhance the uptake of chemotherapeutic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mucoadhesive dexamethasone-glycol chitosan nanoparticles for ophthalmic drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 15;575:118943. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118943. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31830575
-
Self-reporter shikonin-Act-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle: formulation, physicochemical characterization and geno/cytotoxicity evaluation.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Aug 1;59:49-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2014.04.009. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24768857
-
Harnessing hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for combination therapy: A novel approach for suppressing systemic inflammation and to promote antitumor macrophage polarization.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Feb 15;254:117291. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117291. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33357860
-
Nanostructured lipid carriers, solid lipid nanoparticles, and polymeric nanoparticles: which kind of drug delivery system is better for glioblastoma chemotherapy?Drug Deliv. 2016 Nov;23(9):3408-3416. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2016.1189465. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 27181462
-
The rise and rise of stealth nanocarriers for cancer therapy: passive versus active targeting.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2010 Nov;5(9):1415-33. doi: 10.2217/nnm.10.113. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2010. PMID: 21128723 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation, characterization, and transport of dexamethasone-loaded polymeric nanoparticles across a human placental in vitro model.Int J Pharm. 2013 Sep 15;454(1):149-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Jul 12. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23850397 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of surface chemistry on cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of nanocapsules in breast cancer and phagocytic cells.AAPS J. 2014 May;16(3):550-67. doi: 10.1208/s12248-014-9572-0. Epub 2014 Apr 4. AAPS J. 2014. PMID: 24700270 Free PMC article.
-
OCTN2- and ATB0,+-targeted nanoemulsions for improving ocular drug delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Mar 26;22(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02402-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38532399 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles containing anti-inflammatory agents as chemotherapy adjuvants II: role of plasma esterases in drug release.AAPS J. 2009 Mar;11(1):120-2. doi: 10.1208/s12248-009-9086-3. Epub 2009 Feb 19. AAPS J. 2009. PMID: 19225893 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Biocompatibility and Pharmacological Effects of Innovative Systems for Prolonged Drug Release Containing Dexketoprofen in Rats.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Mar 25;13(7):1010. doi: 10.3390/polym13071010. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jain R. K. Transport of molecules in the tumor interstitium: a review. Cancer Res. 1987;47:3039–3051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

