Integrated transcriptomic response to cardiac chronic hypoxia: translation regulators and response to stress in cell survival
- PMID: 18446526
- PMCID: PMC2856931
- DOI: 10.1007/s10142-008-0082-y
Integrated transcriptomic response to cardiac chronic hypoxia: translation regulators and response to stress in cell survival
Abstract
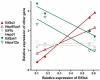
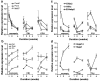
Complementary deoxyribonucleic acid microarray data from 36 mice subjected for 1, 2, or 4 weeks of their early life to normal atmospheric conditions (normoxia) or chronic intermittent (CIH) or constant (CCH) hypoxia were analyzed to extract organizational principles of the developing heart transcriptome and determine the integrated response to oxygen deprivation. Although both CCH and CIH regulated numerous genes involved in a wide diversity of processes, the changes in maturational profile, expression stability, and coordination were vastly different between the two treatments, indicating the activation of distinct regulatory mechanisms of gene transcription. The analysis focused on the main regulators of translation and response to stress because of their role in the cardiac hypertrophy and cell survival in hypoxia. On average, the expression of each heart gene was tied to the expression of about 20% of other genes in normoxia but to only 8% in CCH and 9% in CIH, indicating a strong decoupling effect of hypoxia. In contrast to the general tendency, the interlinkages among components of the translational machinery and response to stress increased significantly in CIH and much more in CCH, suggesting a coordinated response to the hypoxic stress. Moreover, the transcriptomic networks were profoundly and differently remodeled by CCH and CIH.
Figures



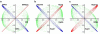
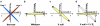
References
-
- Abe K, Tawara S, Oi K, Hizume T, Uwatoku T, Fukumoto Y, Kaibuchi K, Shimokawa H. Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase ameliorates hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2006;48(6):280–285. - PubMed
-
- Alam I, Lewis K, Stephens JW, Baxter JN. Obesity, metabolic syndrome and sleep apnoea: all pro-inflammatory states. Obes Rev. 2007;8(2):119–127. Review. - PubMed
-
- Baker JE. Oxidative stress and adaptation of the infant heart to hypoxia and ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2004;6(2):423–429. Review. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

