Changes in cholesterol kinetics following sugar cane policosanol supplementation: a randomized control trial
- PMID: 18447941
- PMCID: PMC2390548
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-7-17
Changes in cholesterol kinetics following sugar cane policosanol supplementation: a randomized control trial
Abstract
Background: Sugar cane policosanols (SCP) have been shown to exert cholesterol-modulating properties in various studies conducted in Cuba by substantially reducing cholesterol synthesis. Independent research examining changes in cholesterol kinetics in response to SCP is limited to few studies, none of which was able to replicate findings of the original research. Moreover, no data are available on the effect of SCP on cholesterol absorption to date. The present study was undertaken to determine effects on cholesterol kinetics, namely synthesis and absorption, within hypercholesterolemic individuals consuming a SCP treatment. Twenty-one otherwise healthy hypercholesterolemic subjects participated in a randomized double-blind crossover study where they received 10 mg/day of policosanols or a placebo incorporated in margarine as an evening snack for a period of 28 days. The last week of the study phase, subjects were given 13C labelled cholesterol and deuterated water for the measurement of cholesterol absorption and synthesis respectively. Blood was collected on the first two and last five days of the trial. Cholesterol absorption and synthesis were determined by measuring red cell cholesterol 13C and deuterium enrichment, respectively.
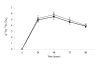
Results: There was no significant change in LDL cholesterol levels as compared to control. In addition, the area under the curve for red cell cholesterol 13C enrichment across 96 hours was not significantly different in the SCP group as compared to control. Similarly, no difference was observed in the fractional rate of cholesterol synthesis over the period of 24 hours between the two treatment groups.
Conclusion: The findings of the present study fail to support previous research concerning efficacy and mechanism of action for policosanols.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sugar cane policosanols do not reduce LDL oxidation in hypercholesterolemic individuals.Lipids. 2009 May;44(5):391-6. doi: 10.1007/s11745-009-3295-5. Epub 2009 Apr 1. Lipids. 2009. PMID: 19337769 Clinical Trial.
-
Lack of cholesterol-lowering efficacy of Cuban sugar cane policosanols in hypercholesterolemic persons.Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Nov;84(5):1003-8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/84.5.1003. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006. PMID: 17093150 Clinical Trial.
-
Cuban Policosanol (Raydel®) Potently Protects the Liver, Ovary, and Testis with an Improvement in Dyslipidemia in Hyperlipidemic Zebrafish: A Comparative Study with Three Chinese Policosanols.Molecules. 2023 Sep 14;28(18):6609. doi: 10.3390/molecules28186609. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37764386 Free PMC article.
-
Policosanol: clinical pharmacology and therapeutic significance of a new lipid-lowering agent.Am Heart J. 2002 Feb;143(2):356-65. doi: 10.1067/mhj.2002.119997. Am Heart J. 2002. PMID: 11835043 Review.
-
Role of policosanols in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.Nutr Rev. 2003 Nov;61(11):376-83. doi: 10.1301/nr.2003.nov.376-383. Nutr Rev. 2003. PMID: 14677572 Review.
Cited by
-
Modified-policosanol does not reduce plasma lipoproteins in hyperlipidemic patients when used alone or in combination with statin therapy.Lipids. 2011 Oct;46(10):923-9. doi: 10.1007/s11745-011-3591-8. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Lipids. 2011. PMID: 21739240 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Menendez R, Amor AM, Gonzalez RM, Fraga V, Mas R. Effect of policosanol on the hepatic cholesterol biosynthesis of normocholesterolemic rats. Biol Res. 1996;29:253–257. - PubMed
-
- Menendez R, Fernandez SI, Del Rio A, Gonzalez RM, Fraga V, Amor AM, Mas RM. Policosanol inhibits cholesterol biosynthesis and enhances low density lipoprotein processing in cultured human fibroblasts. Biol Res. 1994;27:199–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

