Acute-phase reactants after paediatric cardiac arrest. Procalcitonin as marker of immediate outcome
- PMID: 18447945
- PMCID: PMC2386781
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-8-18
Acute-phase reactants after paediatric cardiac arrest. Procalcitonin as marker of immediate outcome
Abstract
Objective: Procalcitonin (PCT) and C reactive protein (CRP) have been used as infection parameters. PCT increase correlates with the infection's severity, course, and mortality. Post-cardiocirculatory arrest syndrome may be related to an early systemic inflammatory response, and may possibly be associated with an endotoxin tolerance. Our objective was to report the time profile of PCT and CRP levels after paediatric cardiac arrest and to assess if they could be use as markers of immediate survival.
Materials and methods: A retrospective observational study set in an eight-bed PICU of a university hospital was performed during a period of two years. Eleven children younger than 14 years were admitted in the PICU after a cardiac arrest. PCT and CRP plasma concentrations were measured within the first 12 and 24 hours of admission.
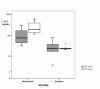
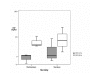
Results: In survivors, PCT values increased 12 hours after cardiac arrest without further increase between 12 and 24 hours. In non survivors, PCT values increased 12 hours after cardiac arrest with further increase between 12 and 24 hours. Median PCT values (range) at 24 hours after cardiac arrest were 22.7 ng/mL (0.2 - 41.0) in survivors vs. 205.5 ng/mL (116.6 - 600.0) in non survivors (p < 0.05). CRP levels were elevated in all patients, survivors and non-survivors, at 12 and 24 hours without differences between both groups.
Conclusion: Measurement of PCT during the first 24 hours after paediatric cardiac arrest could serve as marker of mortality.
Figures

References
-
- Carrol ED, Newland P, Thomson AP, Hart CA. Prognostic value of procalcitonin in children with meningococcal sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:224–225. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000150742.57817.EE. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

