Development of new genomic microsatellite markers from robusta coffee (Coffea canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner) showing broad cross-species transferability and utility in genetic studies
- PMID: 18447947
- PMCID: PMC2396172
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-51
Development of new genomic microsatellite markers from robusta coffee (Coffea canephora Pierre ex A. Froehner) showing broad cross-species transferability and utility in genetic studies
Abstract
Background: Species-specific microsatellite markers are desirable for genetic studies and to harness the potential of MAS-based breeding for genetic improvement. Limited availability of such markers for coffee, one of the most important beverage tree crops, warrants newer efforts to develop additional microsatellite markers that can be effectively deployed in genetic analysis and coffee improvement programs. The present study aimed to develop new coffee-specific SSR markers and validate their utility in analysis of genetic diversity, individualization, linkage mapping, and transferability for use in other related taxa.
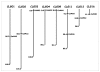
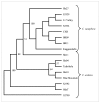
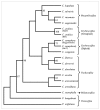
Results: A small-insert partial genomic library of Coffea canephora, was probed for various SSR motifs following conventional approach of Southern hybridisation. Characterization of repeat positive clones revealed a very high abundance of DNRs (1/15 Kb) over TNRs (1/406 kb). The relative frequencies of different DNRs were found as AT >> AG > AC, whereas among TNRs, AGC was the most abundant repeat. The SSR positive sequences were used to design 58 primer pairs of which 44 pairs could be validated as single locus markers using a panel of arabica and robusta genotypes. The analysis revealed an average of 3.3 and 3.78 alleles and 0.49 and 0.62 PIC per marker for the tested arabicas and robustas, respectively. It also revealed a high cumulative PI over all the markers using both sib-based (10-6 and 10-12 for arabicas and robustas respectively) and unbiased corrected estimates (10-20 and 10-43 for arabicas and robustas respectively). The markers were tested for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, linkage dis-equilibrium, and were successfully used to ascertain generic diversity/affinities in the tested germplasm (cultivated as well as species). Nine markers could be mapped on robusta linkage map. Importantly, the markers showed ~92% transferability across related species/genera of coffee.
Conclusion: The conventional approach of genomic library was successfully employed although with low efficiency to develop a set of 44 new genomic microsatellite markers of coffee. The characterization/validation of new markers demonstrated them to be highly informative, and useful for genetic studies namely, genetic diversity in coffee germplasm, individualization/bar-coding for germplasm protection, linkage mapping, taxonomic studies, and use as conserved orthologous sets across secondary genepool of coffee. Further, the relative frequency and distribution of different SSR motifs in coffee genome indicated coffee genome to be relatively poor in microsatellites compared to other plant species.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of genic and genomic SSR markers of robusta coffee (Coffea canephora Pierre Ex A. Froehner).PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e113661. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113661. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25461752 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, characterization and utilization of EST-derived genic microsatellite markers for genome analyses of coffee and related species.Theor Appl Genet. 2007 Jan;114(2):359-72. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0440-x. Epub 2006 Nov 18. Theor Appl Genet. 2007. PMID: 17115127
-
Development of genomic microsatellite markers in Coffea canephora and their transferability to other coffee species.Genome. 2007 Dec;50(12):1156-61. doi: 10.1139/G07-073. Genome. 2007. PMID: 18059542
-
Coffea cytogenetics: from the first karyotypes to the meeting with genomics.Planta. 2022 May 2;255(6):112. doi: 10.1007/s00425-022-03898-z. Planta. 2022. PMID: 35501619 Review.
-
Potential beverage quality of three wild coffee species (Coffea brevipes, C. congensis and C. stenophylla) and consideration of their agronomic use.J Sci Food Agric. 2023 May;103(7):3602-3612. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12347. Epub 2022 Dec 12. J Sci Food Agric. 2023. PMID: 36418192 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic diversity of arabica coffee (Coffea arabica L.) in Nicaragua as estimated by simple sequence repeat markers.ScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:939820. doi: 10.1100/2012/939820. Epub 2012 Jun 4. ScientificWorldJournal. 2012. PMID: 22701376 Free PMC article.
-
Population structure and genetic relationships between Ethiopian and Brazilian Coffea arabica genotypes revealed by SSR markers.Genetica. 2019 Apr;147(2):205-216. doi: 10.1007/s10709-019-00064-4. Epub 2019 May 3. Genetica. 2019. PMID: 31054007
-
Systems Identification and Characterization of Cell Wall Reassembly and Degradation Related Genes in Glycine max (L.) Merill, a Bioenergy Legume.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 7;7(1):10862. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11495-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28883533 Free PMC article.
-
Development of microsatellite markers for identifying Brazilian Coffea arabica varieties.Genet Mol Biol. 2010 Jul;33(3):507-14. doi: 10.1590/S1415-47572010005000055. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Genet Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 21637425 Free PMC article.
-
A high-throughput data mining of single nucleotide polymorphisms in Coffea species expressed sequence tags suggests differential homeologous gene expression in the allotetraploid Coffea arabica.Plant Physiol. 2010 Nov;154(3):1053-66. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.162438. Epub 2010 Sep 23. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20864545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fitter R, Kaplinsky R. Who gains from product rents as the coffee market becomes more differentiated? A value chain analysis. IDS Bulletin (Special Issue) 2001;32:69–82.
-
- Powell W, Machray GC, Provan J. Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1:215–222.
-
- Gupta PK, Varshney RK. The development and use of microsatellite markers for genetic analysis and plant breeding with emphasis on bread wheat. Euphytica. 2000;113:163–185.
-
- Combes MC, Andrzejewski S, Anthony F, Bertrand B, Rovelli P, Graziosi G, Lashermes P. Characterization of microsatellite loci in Coffea arabica and related coffee species. Mol Ecol. 2000;9:1178–1180. - PubMed
-
- Rovelli P, Mettulio R, Anthony F, Anzueto F, Lashermes P, Graziosi G. Microsatellites in Coffea arabica L. In: Sera T, Soccol CR, Pandey A, Roussos S, editor. Coffee Biotechnology and Quality. Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2000. pp. 123–133.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

