Poor condition and infection: a vicious circle in natural populations
- PMID: 18448414
- PMCID: PMC2453294
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2008.0147
Poor condition and infection: a vicious circle in natural populations
Abstract
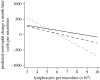
Pathogens may be important for host population dynamics, as they can be a proximate cause of morbidity and mortality. Infection dynamics, in turn, may be dependent on the underlying condition of hosts. There is a clear potential for synergy between infection and condition: poor condition predisposes to host infections, which further reduce condition and so on. To provide empirical data that support this notion, we measured haematological indicators of infection (neutrophils and monocytes) and condition (red blood cells (RBCs) and lymphocytes) in field voles from three populations sampled monthly for 2 years. Mixed-effect models were developed to evaluate two hypotheses, (i) that individuals with low lymphocyte and/or RBC levels are more prone to show elevated haematological indicators of infection when re-sampled four weeks later, and (ii) that a decline in indicators of condition is likely to follow the development of monocytosis or neutrophilia. We found that individuals with low RBC and lymphocyte counts had increased probabilities of developing monocytosis and higher increments in neutrophils, and that high indices of infection (neutrophilia and monocytosis) were generally followed by a declining tendency in the indicators of condition (RBCs and lymphocytes). The vicious circle that these results describe suggests that while pathogens overall may be more important in wildlife dynamics than has previously been appreciated, specific pathogens are likely to play their part as elements of an interactive web rather than independent entities.
Figures


References
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 1974;AC-19:716–723. doi:10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705 - DOI
-
- Alford R.A, Bradfield K.S, Richards S.J. Ecology: global warming and amphibian losses. Nature. 2007;447:E3–E4. doi:10.1038/nature05940 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnard C.J, Behnke J.M, Sewell J. Social status and resistance to disease in house mice (Mus musculus): status-related modulation of immune responses in relation to immunity costs in different social and physiological enviroments. Ethology. 1995;102:63–84.
-
- Barnard C.J, Behnke J.M, Sewell J. Social behaviour stress and susceptibility to infection in house mice (Mus musculus): effects of duration of grouping and aggressive behaviour prior to infection on susceptibility to Babesia microti. Physiol. Behav. 1996;60:1223–1231. doi:10.1016/S0031-9384(96)00174-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Begon M, Townsend C.R, Harper J.L. 4th edn. Blackwell Publishing; Oxford, UK: 2006. Ecology: from individuals to ecosystems.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

