Perturbation of the tRNA tertiary core differentially affects specific steps of the elongation cycle
- PMID: 18448426
- PMCID: PMC2440604
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801560200
Perturbation of the tRNA tertiary core differentially affects specific steps of the elongation cycle
Abstract
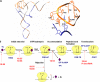
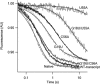
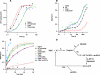
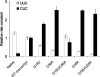
The tRNA tertiary core region is important for both tRNA stability and activity in the translation elongation cycle. Here we report the effects of mutating each of two highly conserved base pairs in the tertiary core of Phe-tRNA(Phe), 18-55 and 19-56, on rate and equilibrium constants for specific steps of this cycle, beginning with formation of aminoacyl-tRNA.EF-Tu.GTP ternary complexs and culminating with translocation of A-site-bound peptidyl-tRNA into the P-site. We find that codon-dependent binding of aminoacyl-tRNA to the A/T-site and proofreading of near-cognate tRNA are sensitive to perturbation of either base pair; formation of the ternary complex and accommodation from the A/T to the A-site are sensitive to 18-55 perturbation only, and translocation of peptidyl-tRNA from the A- to P-site is insensitive to perturbation of either. These results underline the importance of the core region in promoting the efficiency and accuracy of translation, and they likely reflect different requirements for structural integrity of the core during specific steps of the elongation cycle.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GTP consumption of elongation factor Tu during translation of heteropolymeric mRNAs.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):1945-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.1945. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7892205 Free PMC article.
-
The reaction of ribosomes with elongation factor Tu.GTP complexes. Aminoacyl-tRNA-independent reactions in the elongation cycle determine the accuracy of protein synthesis.J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4868-74. J Biol Chem. 1986. PMID: 3514605
-
Elongation factor-Tu can repetitively engage aminoacyl-tRNA within the ribosome during the proofreading stage of tRNA selection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Feb 18;117(7):3610-3620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1904469117. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32024753 Free PMC article.
-
Elongation factor Tu, a GTPase triggered by codon recognition on the ribosome: mechanism and GTP consumption.Biochem Cell Biol. 1995 Nov-Dec;73(11-12):1221-7. doi: 10.1139/o95-132. Biochem Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8722040 Review.
-
Evolutionary optimization of speed and accuracy of decoding on the ribosome.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011 Oct 27;366(1580):2979-86. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0138. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21930591 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of speed and accuracy of decoding in translation.EMBO J. 2010 Nov 3;29(21):3701-9. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.229. Epub 2010 Sep 14. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20842102 Free PMC article.
-
Labeled EF-Tus for rapid kinetic studies of pretranslocation complex formation.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Oct 17;9(10):2421-31. doi: 10.1021/cb500409y. Epub 2014 Aug 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25126896 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule fluorescence measurements of ribosomal translocation dynamics.Mol Cell. 2011 May 6;42(3):367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.03.024. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21549313 Free PMC article.
-
A genetically encoded fluorescent tRNA is active in live-cell protein synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Apr 20;45(7):4081-4093. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27956502 Free PMC article.
-
Twice exploration of tRNA +1 frameshifting in an elongation cycle of protein synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 27;49(17):10046-10060. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab734. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34417618 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frank, J., Sengupta, J., Gao, H., Li, W., Valle, M., Zavialov, A., and Ehrenberg, M. (2005) FEBS Lett. 579 959-962 - PubMed
-
- Yusupov, M. M., Yusupova, G. Z., Baucom, A., Lieberman, K., Earnest, T. N., Cate, J. H., and Noller, H. F. (2001) Science 292 883-896 - PubMed
-
- Korostelev, A., Trakhanov, S., Laurberg, M., and Noller, H. F. (2006) Cell 126 1065-1077 - PubMed
-
- Selmer, M., Dunham, C. M., Murphy, F. V. T., Weixlbaumer, A., Petry, S., Kelley, A. C., Weir, J. R., and Ramakrishnan, V. (2006) Science 313 1935-1942 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

