GIT1 paxillin-binding domain is a four-helix bundle, and it binds to both paxillin LD2 and LD4 motifs
- PMID: 18448431
- PMCID: PMC2441563
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801274200
GIT1 paxillin-binding domain is a four-helix bundle, and it binds to both paxillin LD2 and LD4 motifs
Abstract
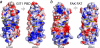
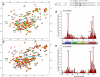
The G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein 1 (GIT1) is a multidomain protein that plays an important role in cell adhesion, motility, cytoskeletal remodeling, and membrane trafficking. GIT1 mediates the localization of the p21-activated kinase (PAK) and PAK-interactive exchange factor to focal adhesions, and its activation is regulated by the interaction between its C-terminal paxillin-binding domain (PBD) and the LD motifs of paxillin. In this study, we determined the solution structure of rat GIT1 PBD by NMR spectroscopy. The PBD folds into a four-helix bundle, which is structurally similar to the focal adhesion targeting and vinculin tail domains. Previous studies showed that GIT1 interacts with paxillin through the LD4 motif. Here, we demonstrated that in addition to the LD4 motif, the GIT1 PBD can also bind to the paxillin LD2 motif, and both LD2 and LD4 motifs competitively target the same site on the PBD surface. We also revealed that paxillin Ser(272) phosphorylation does not influence GIT1 PBD binding in vitro. These results are in agreement with the notion that phosphorylation of paxillin Ser(272) plays an essential role in regulating focal adhesion turnover.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of the target-binding mode of the G protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein in the regulation of focal adhesion dynamics.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 12;294(15):5827-5839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006915. Epub 2019 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30737283 Free PMC article.
-
GIT1 utilizes a focal adhesion targeting-homology domain to bind paxillin.Cell Signal. 2007 Aug;19(8):1733-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.03.010. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17467235 Free PMC article.
-
Structural features of the focal adhesion kinase-paxillin complex give insight into the dynamics of focal adhesion assembly.Protein Sci. 2005 Mar;14(3):644-52. doi: 10.1110/ps.041107205. Epub 2005 Feb 2. Protein Sci. 2005. PMID: 15689512 Free PMC article.
-
Paxillin: a focal adhesion-associated adaptor protein.Oncogene. 2001 Oct 1;20(44):6459-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204786. Oncogene. 2001. PMID: 11607845 Review.
-
Role of the cytoskeletal protein paxillin in oncogenesis.Crit Rev Oncog. 2000;11(1):63-76. Crit Rev Oncog. 2000. PMID: 10795627 Review.
Cited by
-
Liprin-α-Mediated Assemblies and Their Roles in Synapse Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 19;9:653381. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.653381. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin-mediated Signaling via Paxillin-GIT1-PIX Promotes Localized Rac Activation at the Leading Edge and Cell Migration.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 1;11(2):345-352. doi: 10.7150/jca.32853. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31897230 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and mechanistic insights into the interaction between Pyk2 and paxillin LD motifs.J Mol Biol. 2014 Dec 12;426(24):3985-4001. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.08.014. Epub 2014 Aug 29. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25174335 Free PMC article.
-
Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin.Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007. Structure. 2008. PMID: 18940607 Free PMC article.
-
Specific dephosphorylation at tyr-554 of git1 by ptprz promotes its association with paxillin and hic-5.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 5;10(3):e0119361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119361. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25742295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jockusch, B. M., Bubeck, P., Giehl, K., Kroemker, M., Moschner, J., Rothkegel, M., Rudiger, M., Schluter, K., Stanke, G., and Winkler, J. (1995) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 11 379–416 - PubMed
-
- Sastry, S. K., and Burridge, K. (2000) Exp. Cell Res. 261 25–36 - PubMed
-
- Cary, L. A., and Guan, J. L. (1999) Front. Biosci. 4 D102–D113 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

