Identification of a new motif required for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment): the RRRY motif is necessary for the binding of single-stranded DNA substrate and the template strand of the mismatched duplex
- PMID: 18448432
- PMCID: PMC2440594
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M801053200
Identification of a new motif required for the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment): the RRRY motif is necessary for the binding of single-stranded DNA substrate and the template strand of the mismatched duplex
Abstract
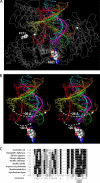
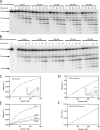
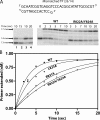
The Klenow fragment of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I houses catalytic centers for both polymerase and 3'-5' exonuclease activities that are separated by about 35 A. Upon the incorporation of a mismatched nucleotide, the primer terminus is transferred from the polymerase site to an exonuclease site designed for excision of the mismatched nucleotides. The structural comparison of the binary complexes of DNA polymerases in the polymerase and the exonuclease modes, together with a molecular modeling of the template strand overhang in Klenow fragment, indicated its binding in the region spanning residues 821-824. Since these residues are conserved in the "A" family DNA polymerases, we have designated this region as the RRRY motif. The alanine substitution of individual amino acid residues of this motif did not change the polymerase activity; however, the 3'-5' exonuclease activity was reduced 2-29-fold, depending upon the site of mutation. The R821A and R822A/Y824A mutant enzymes showed maximum cleavage defect with single-stranded DNA, mainly due to a large decrease in the ssDNA binding affinity of these enzymes. Mismatch removal by these enzymes was only moderately affected. However, data from the exonuclease-polymerase balance assays with mismatched template-primer suggest that the mutant enzymes are defective in switching mismatched primer from the polymerase to the exonuclease site. Thus, the RRRY motif provides a binding track for substrate ssDNA and for nonsubstrate single-stranded template overhang, in a polarity-dependent manner. This binding then facilitates cleavage of the substrate at the exonuclease site.
Figures




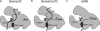
Similar articles
-
Contribution of polar residues of the J-helix in the 3'-5' exonuclease activity of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment): Q677 regulates the removal of terminal mismatch.Biochemistry. 2005 Jun 7;44(22):8101-10. doi: 10.1021/bi050140r. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15924429
-
Primer-terminus stabilization at the 3'-5' exonuclease active site of phi29 DNA polymerase. Involvement of two amino acid residues highly conserved in proofreading DNA polymerases.EMBO J. 1996 Mar 1;15(5):1182-92. EMBO J. 1996. PMID: 8605889 Free PMC article.
-
3'-5' exonuclease of Klenow fragment: role of amino acid residues within the single-stranded DNA binding region in exonucleolysis and duplex DNA melting.Biochemistry. 2002 Mar 26;41(12):3943-51. doi: 10.1021/bi0120603. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 11900537
-
The proofreading 3'-->5' exonuclease activity of DNA polymerases: a kinetic barrier to translesion DNA synthesis.Mutat Res. 2002 Dec 29;510(1-2):45-54. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(02)00251-8. Mutat Res. 2002. PMID: 12459442 Review.
-
DNA polymerases drive DNA sequencing-by-synthesis technologies: both past and present.Front Microbiol. 2014 Jun 24;5:305. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00305. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25009536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and functional study of DNA polymerases from Psychrobacillus sp. BL-248-WT-3 and FJAT-21963.Front Microbiol. 2024 Nov 20;15:1501020. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1501020. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39633807 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamics of the DNA structural selectivity of the Pol I DNA polymerases from Escherichia coli and Thermus aquaticus.Biophys J. 2010 Jun 16;98(12):3015-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.03.021. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 20550914 Free PMC article.
-
Family A and B DNA Polymerases in Cancer: Opportunities for Therapeutic Interventions.Biology (Basel). 2018 Jan 2;7(1):5. doi: 10.3390/biology7010005. Biology (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29301327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis for the dsRNA specificity of the Lassa virus NP exonuclease.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044211. Epub 2012 Aug 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22937163 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering psychrophilic polymerase for nanopore long-read sequencing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 1;12:1406722. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1406722. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39011153 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

