Molecular basis of cytotoxicity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) in EBV latency III B cells: LMP1 induces type II ligand-independent autoactivation of CD95/Fas with caspase 8-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 18448526
- PMCID: PMC2447067
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02250-07
Molecular basis of cytotoxicity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) in EBV latency III B cells: LMP1 induces type II ligand-independent autoactivation of CD95/Fas with caspase 8-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
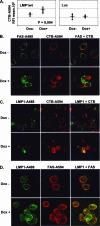
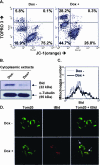
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncoprotein latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is thought to act as the major transforming protein in various cell types, by rerouting the tumor necrosis factor receptor family signaling pathway. Despite this implication in EBV-associated transformation of cells, LMP1 toxicity is a well-known but poorly studied feature, perhaps because it contradicts its role in transformation. We show that LMP1 physiological levels are very heterogeneous and that the highest levels of LMP1 correlate with Fas overexpression and spontaneous apoptosis in lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs). To understand the cytotoxic effect of LMP1 in LCLs, we cloned wild-type LMP1 into a doxycycline double-inducible episomal vector pRT-1, with a truncated version of NGFR as a surrogate marker of inducibility. We found that LMP1 overexpression induced apoptosis in LCL B cells, as shown by annexin V labeling, sub-G(1) peak, and poly(ADP ribose) polymerase cleavage. Knocking down Fas expression by small interfering RNA abolished LMP1-induced apoptosis. The absence of detectable levels of Fas ligand mRNA suggested a ligand-independent activation of Fas. LMP1 induced Fas overexpression with its relocalization in lipid raft microdomains of the membrane. Fas immunoprecipitation detected FADD (Fas-associated death domain protein) and caspase 8, suggesting a Fas-dependent formation of the death-inducing signaling complex. Caspases 8, 9, 3, and 7 were activated by LMP1. Caspase 8 activation was associated with BID cleavage and truncated-BID mitochondrial relocalization, consistent with type II apoptosis. Therefore, our results are in agreement with a model where LMP1-dependent NF-kappaB activation induces Fas overexpression and autoactivation that could overwhelm the antiapoptotic effect of NF-kappaB, revealing an ambivalent function of LMP1 in cell survival and programmed cell death.
Figures






Similar articles
-
EBV latency III immortalization program sensitizes B cells to induction of CD95-mediated apoptosis via LMP1: role of NF-kappaB, STAT1, and p53.Blood. 2006 Mar 1;107(5):2070-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-05-2053. Epub 2005 Nov 29. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16317104
-
EBV LMP2A affects LMP1-mediated NF-kappaB signaling and survival of lymphoma cells by regulating TRAF2 expression.Blood. 2008 Apr 1;111(7):3813-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-080309. Epub 2008 Jan 29. Blood. 2008. PMID: 18230756 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the mutated Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1(69del): implications for a new role of naturally occurring LMP1 variants.Haematologica. 2003 Dec;88(12):1324-35. Haematologica. 2003. PMID: 14687985
-
Cell survival and death program modulated by LMP1: implication in antitumor immunity.Ai Zheng. 2009 Aug;28(8):831-7. doi: 10.5732/cjc.009.10077. Ai Zheng. 2009. PMID: 19664329 Review.
-
Epstein-barr virus transformation: involvement of latent membrane protein 1-mediated activation of NF-kappaB.Oncogene. 1999 Nov 22;18(49):6959-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203217. Oncogene. 1999. PMID: 10602470 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinctive effects of the Epstein-Barr virus family of repeats on viral latent gene promoter activity and B-lymphocyte transformation.J Virol. 2009 Sep;83(18):9163-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01979-08. Epub 2009 Jul 1. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19570868 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2 specific T-cell receptors driven by T-cell specific promoters using lentiviral vector.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:716926. doi: 10.1155/2011/716926. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21969838 Free PMC article.
-
RelA and RelB cross-talk and function in Epstein-Barr virus transformed B cells.Leukemia. 2014 Apr;28(4):871-9. doi: 10.1038/leu.2013.274. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Leukemia. 2014. PMID: 24056880
-
LMP1-deficient Epstein-Barr virus mutant requires T cells for lymphomagenesis.J Clin Invest. 2015 Jan;125(1):304-15. doi: 10.1172/JCI76357. Epub 2014 Dec 8. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25485679 Free PMC article.
-
An Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) mutant with enhanced BZLF1 expression causes lymphomas with abortive lytic EBV infection in a humanized mouse model.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):7976-87. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00770-12. Epub 2012 May 23. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22623780 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baran-Marszak, F., J. Feuillard, I. Najjar, C. Le Clorennec, J. Béchet, I. Dusanter-Fourt, G. W. Bornkamm, M. Raphaël, and R. Fagard. 2004. Differential roles of STAT1α and STAT1β in fludarabine-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human B cells. Blood 1042475-2483. - PubMed
-
- Bornkamm, G. W., C. Berens, C. Kuklik-Roos, J. Bechet, G. Laux, J. Bachl, M. Korndoerfer, M. Schlee, M. Hölzel, A. Malamoussi, R. D. Chapman, F. Nimmerjahn, J. Mautner, W. Hillen, H. Bujard, and J. Feuillard. 2005. Stringent doxycycline-dependent control of gene activities using an episomal one-vector system. Nucleic Acids Res. 33e137. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Busch, L. K., and G. A. Bishop. 1999. The EBV transforming protein, latent membrane protein 1, mimics and cooperates with CD40 signaling in B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1622555-2561. - PubMed
-
- Canman, C. E., and M. B. Kastan. 1995. Induction of apoptosis by tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes. Semin. Cancer Biol. 617-25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

