Interactions of murine APOBEC3 and human APOBEC3G with murine leukemia viruses
- PMID: 18448535
- PMCID: PMC2447093
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01357-07
Interactions of murine APOBEC3 and human APOBEC3G with murine leukemia viruses
Abstract
APOBEC3 proteins are cytidine deaminases which help defend cells against retroviral infections. One antiviral mechanism involves deaminating dC residues in minus-strand DNA during reverse transcription, resulting in G-to-A mutations in the coding strand. We investigated the effects of mouse APOBEC3 (mA3) and human APOBEC3G (hA3G) upon Moloney murine leukemia virus (MLV). We find that mA3 inactivates MLV but is significantly less effective against MLV than is hA3G. In contrast, mA3 is as potent against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1, lacking the protective Vif protein) as is hA3G. The two APOBEC3 proteins are packaged to similar extents in MLV particles. Dose-response profiles imply that a single APOBEC3 molecule (or oligomer) is sufficient to inactivate an MLV particle. The inactivation of MLV by mA3 and hA3G is accompanied by relatively small reductions in the amount of viral DNA in infected cells. Although hA3G induces significant levels of G-to-A mutations in both MLV and HIV DNAs, and mA3 induces these mutations in HIV DNA, no such mutations were detected in DNA synthesized by MLV inactivated by mA3. Thus, MLV has apparently evolved to partially resist the antiviral effects of mA3 and to totally resist the ability of mA3 to induce G-to-A mutation in viral DNA. Unlike the resistance of HIV-1 and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 to hA3G, the resistance of MLV to mA3 is not mediated by the exclusion of APOBEC from the virus particle. The nature of its resistance and the mechanism of inactivation of MLV by mA3 are completely unknown.
Figures

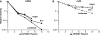
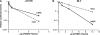






References
-
- Abudu, A., A. Takaori-Kondo, T. Izumi, K. Shirakawa, M. Kobayashi, A. Sasada, K. Fukunaga, and T. Uchiyama. 2006. Murine retrovirus escapes from murine APOBEC3 via two distinct novel mechanisms. Curr. Biol. 161565-1570. - PubMed
-
- Albritton, L. M., L. Tseng, D. Scadden, and J. M. Cunningham. 1989. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell 57659-666. - PubMed
-
- Bassin, R. H., N. Tuttle, and P. J. Fischinger. 1971. Rapid cell culture assay for murine leukaemia virus. Nature 229564-566. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, K. N., R. K. Holmes, A. M. Sheehy, N. O. Davidson, S. J. Cho, and M. H. Malim. 2004. Cytidine deamination of retroviral DNA by diverse APOBEC proteins. Curr. Biol. 141392-1396. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

