Mechanism of urinary calcium regulation by urinary magnesium and pH
- PMID: 18448585
- PMCID: PMC2488265
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2007091038
Mechanism of urinary calcium regulation by urinary magnesium and pH
Abstract
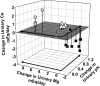
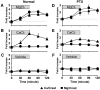
Urinary magnesium and pH are known to modulate urinary calcium excretion, but the mechanisms underlying these relationships are unknown. In this study, the data from 17 clinical trials in which urinary magnesium and pH were pharmacologically manipulated were analyzed, and it was found that the change in urinary calcium excretion is directly proportional to the change in magnesium excretion and inversely proportional to the change in urine pH; a regression equation was generated to relate these variables (R(2) = 0.58). For further exploration of these relationships, intravenous calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, or vehicle was administered to rats. Magnesium infusion significantly increased urinary calcium excretion (normalized to urinary creatinine), but calcium infusion did not affect magnesium excretion. Parathyroidectomy did not prevent this magnesium-induced hypercalciuria. The effect of magnesium loading on calciuria was still observed after treatment with furosemide, which disrupts calcium and magnesium absorption in the thick ascending limb, suggesting that the effect may be mediated by the distal nephron. The calcium channel TRPV5, normally present in the distal tubule, was expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Calcium uptake by TRPV5 was directly inhibited by magnesium and low pH. In summary, these data are compatible with the hypothesis that urinary magnesium directly inhibits renal calcium absorption, which can be negated by high luminal pH, and that this regulation likely takes place in the distal tubule.
Figures

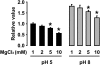
Similar articles
-
Variations of dietary salt and fluid modulate calcium and magnesium transport in the renal distal tubule.Nephron Physiol. 2012;122(3-4):19-27. doi: 10.1159/000353199. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Nephron Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23774784 Free PMC article.
-
Renal calcium and magnesium excretion during vasopressin administration into sheep with acid or alkaline urine.J Physiol. 1979 Sep;294:223-38. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012927. J Physiol. 1979. PMID: 41939 Free PMC article.
-
Increased renal calcium and magnesium transporter abundance in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus.Kidney Int. 2006 May;69(10):1786-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000344. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16557223
-
Regulation of renal calbindin-D28K.Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000;87 Suppl 3:5-30. Pharmacol Toxicol. 2000. PMID: 11097107 Review.
-
Common variants in CLDN14 are associated with differential excretion of magnesium over calcium in urine.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Jan;469(1):91-103. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1913-7. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 27915449 Review.
Cited by
-
The importance of kidney calcium handling in the homeostasis of extracellular fluid calcium.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Aug;474(8):885-900. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02725-4. Epub 2022 Jul 16. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35842482 Review.
-
Magnesium sulfate toxicity successfully managed with hemodialysis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 22;19(1):357. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05430-9. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40696447 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants and Outcomes Associated With Urinary Calcium Excretion in Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan 1;107(1):e281-e292. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgab574. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 34390334 Free PMC article.
-
SLC26 Cl-/HCO3- exchangers in the kidney: roles in health and disease.Kidney Int. 2013 Oct;84(4):657-66. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.138. Epub 2013 May 1. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23636174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demographic, dietary, and urinary factors and 24-h urinary calcium excretion.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Dec;4(12):1980-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02620409. Epub 2009 Oct 9. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19820135 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman PA: Renal calcium metabolism. In: The Kidney: Physiology and Physiopathology, 3rd Ed., edited by Giebisch G, Seldin DW, Philadelphia, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000, pp 1749–1778
-
- Robertson WG, Morgan DB: The distribution of urinary calcium excretions in normal persons and stone-formers. Clin Chim Acta 37: 503–508, 1972 - PubMed
-
- Mendel L, Benedict S: The paths of excretion for inorganic compounds: The excretion of magnesium. Am J Physiol XXV: 1–22, 1909
-
- Cruikshank DP, Pitkin RM, Donnelly E, Reynolds WA: Urinary magnesium, calcium, and phosphate excretion during magnesium sulfate infusion. Obstet Gynecol 58: 430–434, 1981 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

