Nucleophosmin is a binding partner of nucleostemin in human osteosarcoma cells
- PMID: 18448670
- PMCID: PMC2441661
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0128
Nucleophosmin is a binding partner of nucleostemin in human osteosarcoma cells
Abstract
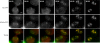
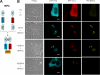
Nucleostemin (NS) is expressed in the nucleoli of adult and embryonic stem cells and in many tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. In coimmunoprecipitation experiments, nucleostemin is recovered with the tumor suppressor p53, and more recently we have demonstrated that nucleostemin exerts its role in cell cycle progression via a p53-dependent pathway. Here, we report that in human osteosarcoma cells, nucleostemin interacts with nucleophosmin, a nucleolar protein believed to possess oncogenic potential. Nucleostemin (NS) and nucleophosmin (NPM) displayed an extremely high degree of colocalization in the granular component of the nucleolus during interphase, and both proteins associated with prenucleolar bodies in late mitosis before the reformation of nucleoli. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments revealed that NS and NPM co-reside in complexes, and yeast two-hybrid experiments confirmed that they are interactive proteins, revealing the NPM-interactive region to be the 46-amino acid N-terminal domain of NS. In bimolecular fluorescence complementation studies, bright nucleolar signals were observed, indicating that these two proteins directly interact in the nucleolus in vivo. These results support the notion that cell cycle regulatory proteins congress and interact in the nucleolus, adding to the emerging concept that this nuclear domain has functions beyond ribosome production.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A nonribosomal landscape in the nucleolus revealed by the stem cell protein nucleostemin.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3401-10. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-02-0106. Epub 2005 Apr 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15857956 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleoplasmic mobilization of nucleostemin stabilizes MDM2 and promotes G2-M progression and cell survival.J Cell Sci. 2008 Dec 15;121(Pt 24):4037-46. doi: 10.1242/jcs.037952. Epub 2008 Nov 25. J Cell Sci. 2008. PMID: 19033382 Free PMC article.
-
A multistep, GTP-driven mechanism controlling the dynamic cycling of nucleostemin.J Cell Biol. 2005 Jan 17;168(2):179-84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200409053. J Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657390 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the nucleolus in regulating the cell cycle and the DNA damage response.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2023;135:203-241. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2023.01.001. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2023. PMID: 37061332 Review.
-
The nucleolus: a model for the organization of nuclear functions.Histochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;126(2):135-48. doi: 10.1007/s00418-006-0212-3. Epub 2006 Jul 12. Histochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16835752 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs with a nucleolar location.RNA. 2009 Sep;15(9):1705-15. doi: 10.1261/rna.1470409. Epub 2009 Jul 23. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19628621 Free PMC article.
-
The Nucleolus Takes Control of Protein Trafficking Under Cellular Stress.Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2010;2(5):203-212. Mol Cell Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 21499571 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of the Drosophila GTPase nucleostemin 1 impairs large ribosomal subunit biogenesis, cell growth, and midgut precursor cell maintenance.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Oct;20(20):4424-34. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0592. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19710426 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor PNRC1 blocks rRNA maturation by recruiting the decapping complex to the nucleolus.EMBO J. 2018 Dec 3;37(23):e99179. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899179. Epub 2018 Oct 29. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 30373810 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of caveolin-1 drives estrogen-hypersensitivity and the development of DCIS-like mammary lesions.Am J Pathol. 2009 Apr;174(4):1172-90. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.080882. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19342371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen J. S., Lyon C. E., Fox A. H., Leung A.K.L., Lam Y. W., Steen H., Mann M., Lamond A. I. Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus. Curr. Biol. 2002;12:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Boisvert F.-M., van Koningsbruggen S., Navascues J., Lamond A. I. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nature. 2007;8:574–585. - PubMed
-
- Chan P. K., Chan F. Y. Nucleophosmin/B23 (NPM) oligomer is a major and stable entity in HeLa cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1995;1262:37–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

