Age-dependent loss of sperm production in mice via impaired lysophosphatidic acid signaling
- PMID: 18448840
- PMCID: PMC2574971
- DOI: 10.1095/biolreprod.108.068783
Age-dependent loss of sperm production in mice via impaired lysophosphatidic acid signaling
Abstract
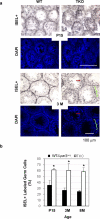
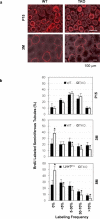
Approximately half of all infertility cases can be attributed to male reproductive dysfunction for which low sperm count is a major contributing factor. The current study identified receptor-mediated lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling as a new molecular component influencing male fertility. LPA is a small signaling phospholipid, the effects of which are mediated through at least five G protein-coupled receptors, named LPA 1-5. LPA1/2/3, but not LPA4/5, show high expression in mouse testis. Mice deficient in LPA1/2/3 showed a testosterone-independent reduction of mating activity and sperm production, with an increased prevalence of azoospermia in aging animals. A significant increase of germ cell apoptosis also was observed in testes. Germ cell apoptosis led to a reduction in germ cell proliferation. These data demonstrate a novel in vivo function for LPA signaling as a germ cell survival factor during spermatogenesis.
Figures
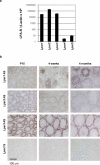
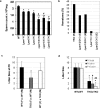
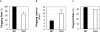
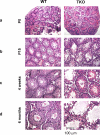

References
-
- Ishii I, Fukushima N, Ye X, Chun J.Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu Rev Biochem 2004; 73: 321–354. - PubMed
-
- Budnik LT, Mukhopadhyay AK.Lysophosphatidic acid and its role in reproduction. Biol Reprod 2002; 66: 859–865. - PubMed
-
- Fukushima N, Ishii I, Contos JJ, Weiner JA, Chun J.Lysophospholipid receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2001; 41: 507–534. - PubMed
-
- Gaits F, Fourcade O, Le Balle F, Gueguen G, Gaige B, Gassama-Diagne A, Fauvel J, Salles JP, Mauco G, Simon MF, Chap H.Lysophosphatidic acid as a phospholipid mediator: pathways of synthesis. FEBS Lett 1997; 410: 54–58. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Xiao YJ, Zhu K, Baudhuin LM, Lu J, Hong G, Kim KS, Cristina KL, Song L, Williams FS, Elson P, Markman M, Belinson J.Unfolding the pathophysiological role of bioactive lysophospholipids. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metab Disord 2003; 3: 23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

