Effects of echinacea on the frequency of upper respiratory tract symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 18450126
- PMCID: PMC7129680
- DOI: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60603-5
Effects of echinacea on the frequency of upper respiratory tract symptoms: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Upper respiratory tract infection symptoms are a common cause of morbidity. Herbal preparations of the plant Echinacea purpurea have immune-enhancing properties.
Objective: To compare the frequency of upper respiratory tract symptoms in individuals receiving E. purpurea capsules and those receiving placebo to evaluate the preventive efficacy of echinacea.
Methods: In a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, 90 volunteers recruited from hospital personnel were randomly assigned to receive 3 capsules twice daily of either placebo (parsley) or E. purpurea for 8 weeks during the winter months. Upper respiratory tract symptoms were reported weekly during this period.
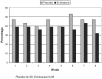
Results: Fifty-eight individuals were included in the final data analysis: 28 in the echinacea group and 30 in the placebo group. Individuals in the echinacea group reported 9 sick days per person during the 8-week period, whereas the placebo group reported 14 sick days (z = -0.42; P = .67). Mild adverse effects were noted by 8% of the echinacea group and 7% of the placebo group (P = .24).
Conclusion: Prophylactic treatment with commercially available E. purpurea capsules did not significantly alter the frequency of upper respiratory tract symptoms compared with placebo use.
Figures
References
-
- Mossad SB, Macknin ML, Medendorp SV, Mason P. Zinc gluconate lozenges for treating the common cold: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann Intern Med. 1996;125:81–88. - PubMed
-
- Gwaltney JM, Jr, Hendley JO, Simon G, Jordan WS., Jr Rhinovirus infections in an industrial population, I: the occurrence of illness. N Engl J Med. 1966;275:1261–1268. - PubMed
-
- Sun LZ, Currier NL, Miller SC. The American coneflower: a prophylactic role involving nonspecific immunity. J Altern Complement Med. 1999;5:437–446. - PubMed
-
- Wustenberg P, Henneicke-von Zepelin HH, Kohler G, Stammwitz U. Efficacy and mode of action of an immunomodulator herbal preparation containing Echinacea, wild indigo, and white cedar. Adv Ther. 1999;16:51–70. - PubMed
-
- Percival SS. Use of echinacea in medicine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000;60:155–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources