MicroRNA-155 is a negative regulator of activation-induced cytidine deaminase
- PMID: 18450484
- PMCID: PMC2430982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.03.015
MicroRNA-155 is a negative regulator of activation-induced cytidine deaminase
Abstract
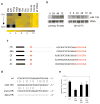
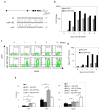
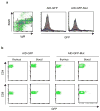
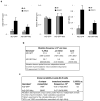
B lymphocytes perform somatic hypermutation and class-switch recombination (CSR) of the immunoglobulin locus to generate an antibody repertoire diverse in both affinity and function. These somatic diversification processes are catalyzed by activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a potent DNA mutator whose expression and function are highly regulated. Here we show that AID was regulated posttranscriptionally by a lymphocyte-specific microRNA, miR-155. We found that miR-155 was upregulated in murine B lymphocytes undergoing CSR and that it targeted a conserved site in the 3'-untranslated region of the mRNA encoding AID. Disruption of this target site in vivo resulted in quantitative and temporal deregulation of AID expression, along with functional consequences for CSR and affinity maturation. Thus, miR-155, which has recently been shown to play important roles in regulating the germinal-center reaction, does so in part by directly downmodulating AID expression.
Figures

Comment in
-
Along came a spider: AID escapes a microRNA web.Immunity. 2008 May;28(5):596-8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.04.012. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 18482561
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP, Chen CZ. Micromanagers of gene expression: the potentially widespread influence of metazoan microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:396–400. - PubMed
-
- Basu U, Chaudhuri J, Alpert C, Dutt S, Ranganath S, Li G, Schrum JP, Manis JP, Alt FW. The AID antibody diversification enzyme is regulated by protein kinase A phosphorylation. Nature. 2005;438:508–511. - PubMed
-
- Basu U, Chaudhuri J, Phan RT, Datta A, Alt FW. Regulation of activation induced deaminase via phosphorylation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;596:129–137. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri J, Khuong C, Alt FW. Replication protein A interacts with AID to promote deamination of somatic hypermutation targets. Nature. 2004;430:992–998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

